Antrodia cinnamomea Enhances Chemo-Sensitivity of 5-FU and Suppresses Colon Tumorigenesis and Cancer Stemness via Up-Regulation of Tumor Suppressor miR-142-3p
Abstract
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) regimen remains the backbone of the first-line agent to treat colon cancer, but often these patients develop resistance. Cancer stem cells (CSC's) are considered as one of the key contributors in the development of drug resistance and tumor recurrence. We aimed to provide preclinical evidence for Antrodiacinnamomea (AC), as a potential in suppressing colon cancer CSC's to overcome 5-FU drug-resistant. In-vitro assays including cell viability, colony formation, AC + 5-FU drug combination index and tumor sphere generation were applied to determine the inhibitory effect of AC. Mouse xenograft models also incorporated to evaluate in vivo effect of AC. AC treatment significantly inhibited the proliferation, colony formation and tumor sphere generation. AC also inhibited the expression of oncogenic markers (NF-κB, and C-myc), EMT/metastasis markers (vimentin and MMP3) and stemness associated markers (β-catenin, SOX-2 and Nanog). Sequential treatment of AC and 5-FU synergized and reduces colon cancer viability both in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistically, AC mediated anti-tumor effect was associated with an increased level of tumor suppressor microRNAs especially, miR142-3p. AC can be a potent synergistic adjuvant, down-regulates cancer stemness genes and enhances the antitumor ability of 5-FU by stimulating apoptosis-associated genes, suppressing inflammation and metastasis genes through miR142-3p in colon cancer.
Figures 
Figure 1
AC treatment decreases the viability…Figure 1
AC treatment decreases the viability of CRC cells by inducing apoptosis. ( A… Figure 1 AC treatment decreases the viability of CRC cells by inducing apoptosis. (A) Cell viability assay demonstrates that AC is effectively suppressing the cellular viability in CRC cells. The IC50 values of AC in all three cells (SW480, SW620 and HCT116) are indicated. (B) AC effectively suppresses colony-forming ability. *** p < 0.001. (C) Colon cancer cell lines were treated with AC (100 µg/mL) for 24 h and then analyzed for apoptosis by flow cytometer for Annexin-V+ and PI+ stained cells. AC significantly induces apoptosis in CRC cells (SW480, SW620 and HCT116). Number in the box indicates the percentage of Annexin-V+ cells (control versus AC treatment, left and right respectively). (D) Western blots of the whole-cell lysates from AC treated colon cancer cells showed a significantly increased level of cleaved PARP (pro-apoptotic marker).
Figure 2
Suppression of cancer stemness by…
Figure 2
Suppression of cancer stemness by AC treatment. ( A ) Tumor sphere formation…
Figure 2 Suppression of cancer stemness by AC treatment. (A) Tumor sphere formation assay. Colon cancer cells treated with AC (100 µg/mL, 48 h) demonstrated a significant reduction in number of tumor spheres generated under serum-deprived culture conditions. *** p < 0.001. (B) q-PCR analysis showed that AC treatment down-regulated cancer stem cell markers β-catenin, SOX-2, Nanog. ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05. (C) Aldefluor assay showed that AC treatment (100 µg/mL, 48 h) prominently and dose-dependently reduces the ALDH1 enzymatic activity in all three colon cancer cell lines examined.
Figure 3
AC treatment increased 5-FU sensitivity…Figure 3
AC treatment increased 5-FU sensitivity in colon cancer cells. Drug combination assay, different… Figure 3 AC treatment increased 5-FU sensitivity in colon cancer cells. Drug combination assay, different concentrations of AC and 5-FU were used in combination for calculating the combination index (CI). Normalized isobolograms demonstrated a combination of AC and 5-FU synergistically suppressed the cell viability of colon cancer cells. CI values < 1 denotes synergy.
Figure 4
Impact of AC on the…
Figure 4
Impact of AC on the signaling pathway of CRC cell lines. AC (100…
Figure 4 Impact of AC on the signaling pathway of CRC cell lines. AC (100 μg/mL) treatment were given to CRC cells for 24 h. (A) AC significantly decreases the EMT associated β-catenin and vimentin gene expression, (B) suppression of oncogenic markers NF-κb, C-myc and MMP3, and (C) upregulation of miRNA expression, specially miR142-3p, and miR142-3p expression negatively regulates ABCG2. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001.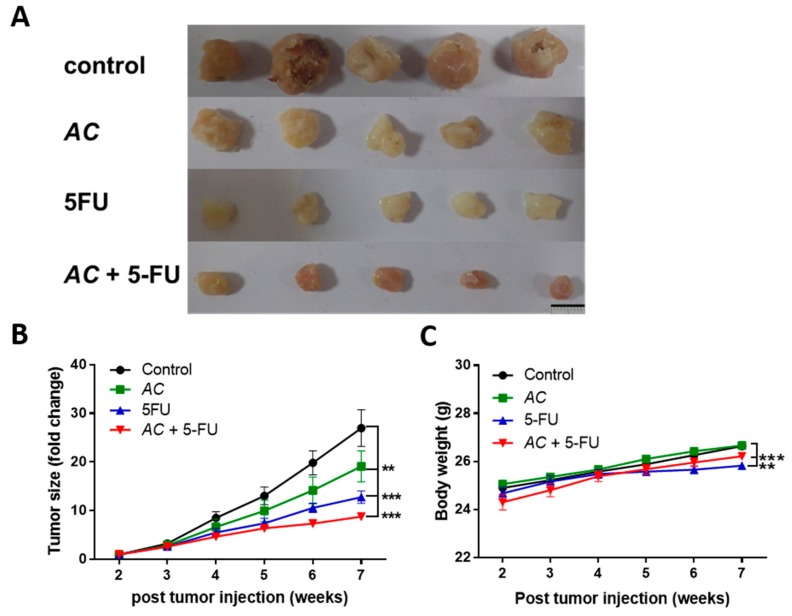
Figure 5
In-vivo tumor inhibitory effect of…
Figure 5
In-vivo tumor inhibitory effect of AC . ( A ) Photographs of human…
Figure 5 In-vivo tumor inhibitory effect of AC. (A) Photographs of human colon cancer cells, DLD-1 (1 × 106 cells/injection, subcutaneous) were injected into NDO/SCD mice for establishing tumor xenograft model. When tumor size became palpable, mice were separated into four groups: Vehicle control, AC (50 mg/Kg), 5-FU (10 mg/kg), and combination AC + 5-FU (30 mg/kg 5-FU + 10 mg/kg AC). (B) Evaluation of tumor suppressive effect, synergistic effect of AC + 5-FU significantly decreases the size of tumor in the combination treatment group followed by AC and 5-FU individual treatment. (C) Averaged body weight of the animals, there is no negative impact of treatment on the body weight of animals, except for the 5-FU group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001.