Antcin-H Isolated from Antrodia cinnamomea Inhibits Renal Cancer Cell Invasion Partly through Inactivation of FAK-ERK-C/EBP- β/c-Fos-MMP-7 Pathways
Figures
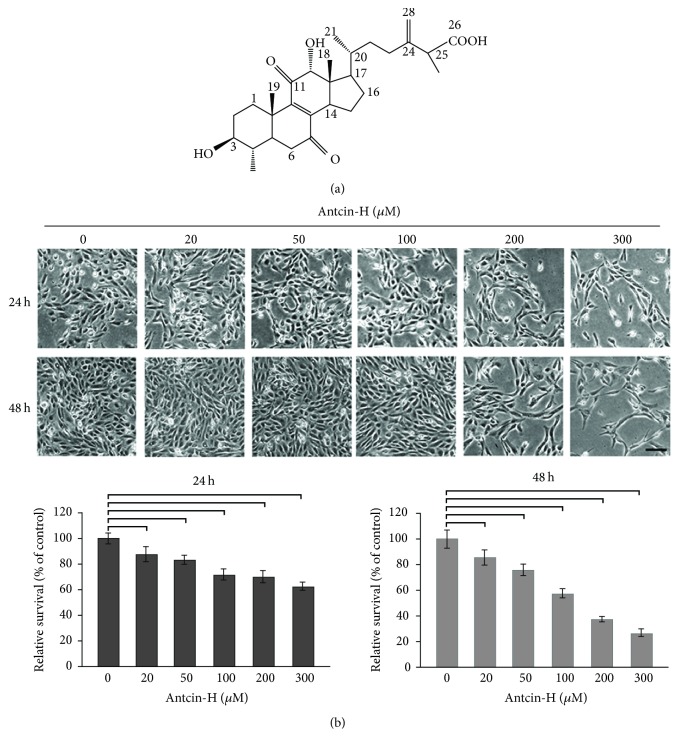
Figure 1
Growth inhibitory effect of antcin-H.…
Figure 1
Growth inhibitory effect of antcin-H. (a) The chemical structure of antcin-H. (b) Human…
Figure 1 Growth inhibitory effect of antcin-H. (a) The chemical structure of antcin-H. (b) Human RCC 786-0 cells were treated with various concentrations (0, 20, 50, 100, 200, and 300 μM) of antcin-H for 24 and 48 h. After incubation, cell morphology was investigated using phase-contrast microscope (upper panel). Scale bar, 100 μm. The cell viability was determined by trypan blue dye exclusion method (lower panel).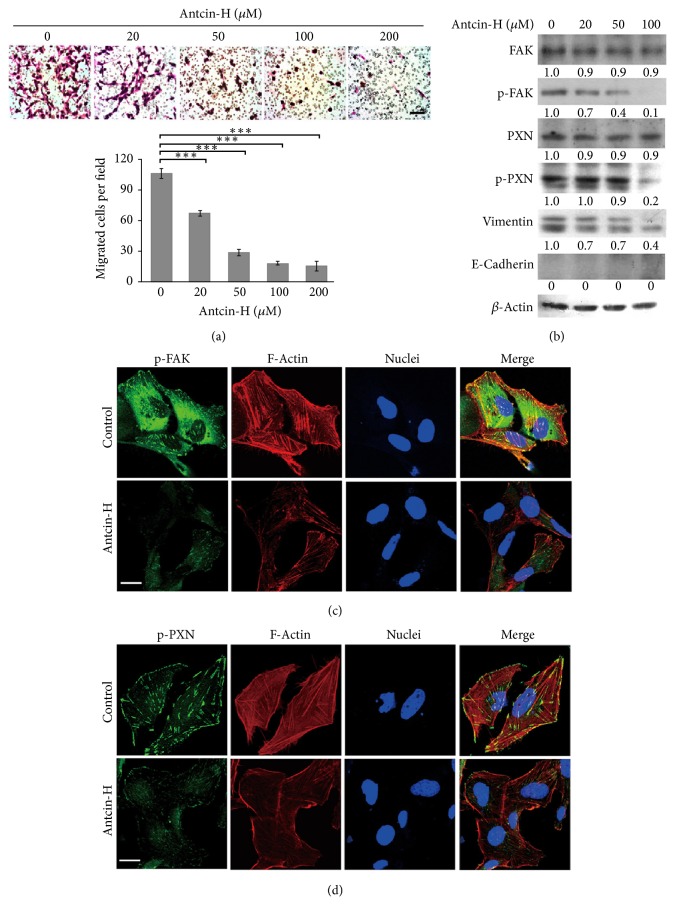
Figure 2
Inhibition of cell migration and…
Figure 2
Inhibition of cell migration and modulation of migration-related proteins by antcin-H in vitro.…
Figure 2 Inhibition of cell migration and modulation of migration-related proteins by antcin-H in vitro. (a) 786-0 cells were treated without or with 20, 50, 100, and 200 μM antcin-H for 24 h, and then cells were seeded in the upper part of Transwell. After 16 h, cells on the bottom side of the filter were microphotographed and counted. Data were represented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistically significant, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Scale bar, 100 μm. (b) Regulation of FAK, paxillin, E-cadherin, and vimentin by antcin-H. 786-0 cells were treated without or with 20, 50, and 100 μM antcin-H for 24 h, and then protein lysates were isolated. The levels of phosphorylated-FAK, phosphorylated-paxillin, E-cadherin, and vimentin were examined by Western blot analysis. β-Actin was used as an internal loading control. Confocal imaging of (c) phosphorylated-FAK and (d) phosphorylated-paxillin. 786-0 cells were treated without or with 100 μM antcin-H for 24 h. The cellular distribution of phosphorylated-FAK and phosphorylated-paxillin was examined by immunofluorescence staining using phosphorylated-FAK and phosphorylated-paxillin specific antibodies. The immunoreactive images were investigated by confocal microscope. Scale bar, 20 μm.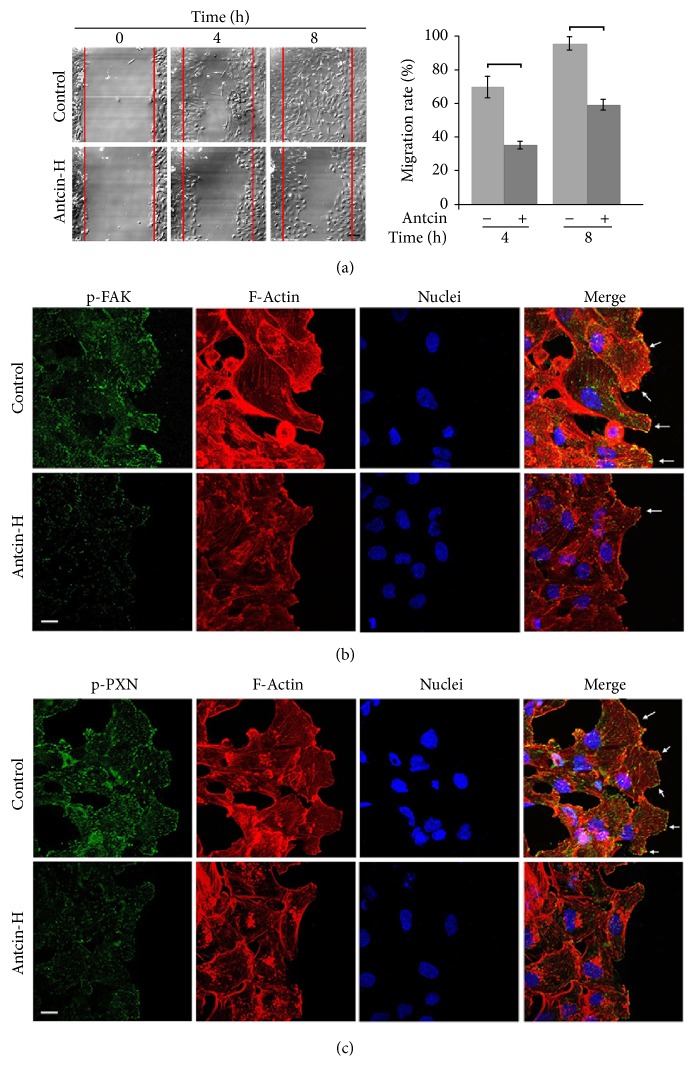
Figure 3
Suppression of wound-healing and disruption…
Figure 3
Suppression of wound-healing and disruption of lamellipodium formation by antcin-H. (a) Live cell…
Figure 3 Suppression of wound-healing and disruption of lamellipodium formation by antcin-H. (a) Live cell time-lapse images at wound-healing front. 786-0 cells were cultured to 100% confluence on glass coverslips. After wound was made, fresh media without or with 100 μM antcin-H were added. Cells were allowed to migrate; the time-lapse of live cell imaging was observed at 4 and 8 h. Scale bar, 20 μm. (b) Immunostaining with FAK or (c) paxillin antibody. After 8 h wounding, the migrated cells were fixed, and the immunofluorescence staining was carried out using anti-phosphorylated-FAK and anti-phosphorylated-paxillin antibodies. The immunoreactive image was recorded by confocal microscope. Arrow, formation of lamellipodium. Scale bar, 20 μm.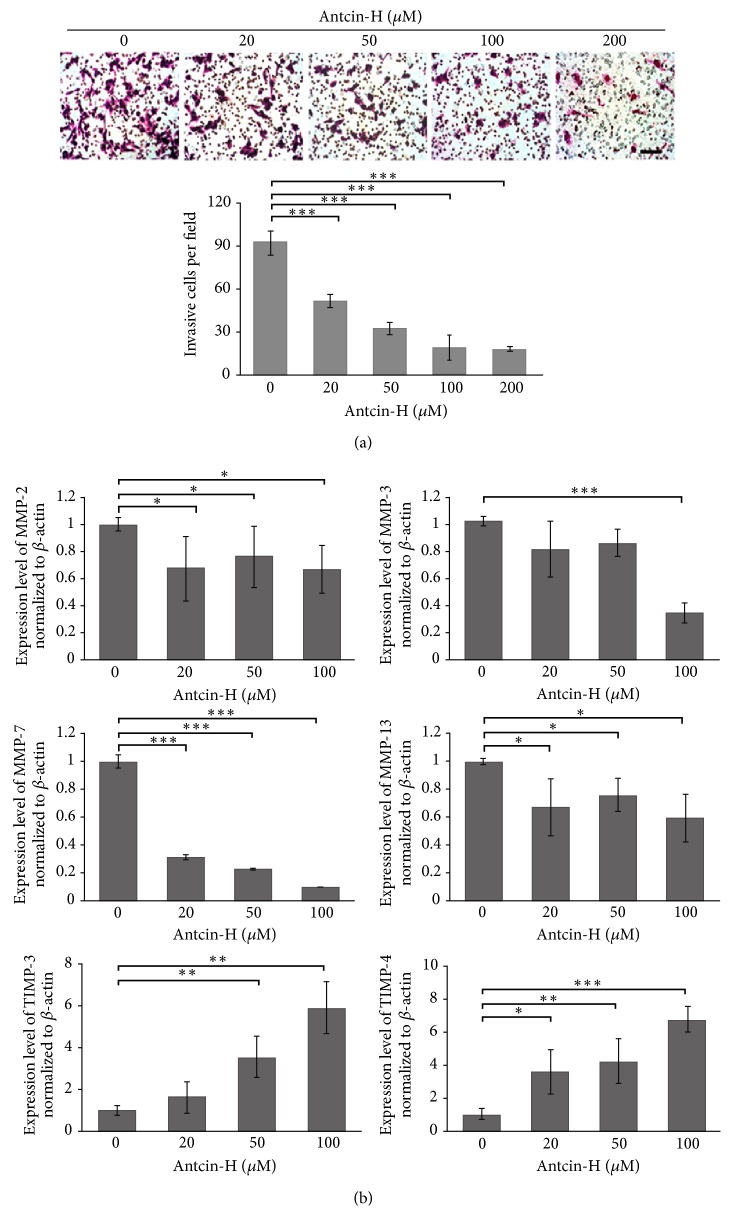
Figure 4
ANTCIN-H prevents invasion and regulates…
Figure 4
ANTCIN-H prevents invasion and regulates MMPs gene expression. (a) 768-0 cells were pretreated…
Figure 4 ANTCIN-H prevents invasion and regulates MMPs gene expression. (a) 768-0 cells were pretreated without or with 20, 50, 100, and 200 μM antcin-H for 24 h and then seeded into Matrigel-coated Transwell apparatus for another 24 h in the absence or presence of antcin-H. After incubation, the invaded cells were stained with Giemsa solution and counted using a microscope. Scale bar, 100 μm. The data were represented as the mean ± SD of nine replicates from three separated experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control. (b) Real-time PCR analysis of MMPs and TIMPs gene expression. Cells were treated without or with 20, 50, and 100 μM antcin-H for 24 h. After treatment, the RNA extracted from 786-0 cells was subjected to a real-time PCR. β-Actin was used as an internal control. Data were represented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistically significant, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.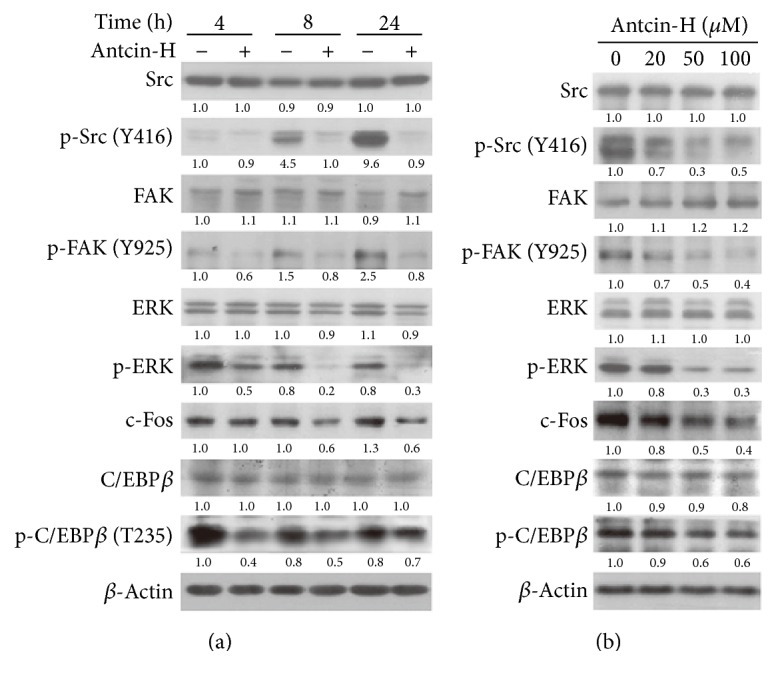
Figure 5
Suppression of Src, FAK, and…
Figure 5
Suppression of Src, FAK, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways by antcin-H. (a) Time course-dependent…
Figure 5 Suppression of Src, FAK, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways by antcin-H. (a) Time course-dependent experiment. 786-0 cells were treated without or with 100 μM antcin-H for 4, 8, and 24 h. (b) Dose-dependent experiment. Cells were treated without or with 20, 50, and 100 μM antcin-H for 24 h. After incubation, total protein lysates were isolated; the Western blotting analysis was performed to examine the levels of phosphorylated-Src, phosphorylated-FAK, phosphorylated-ERK1/2, phosphorylated-C/EBP-β, and c-Fos. β-Actin was used as an internal loading control.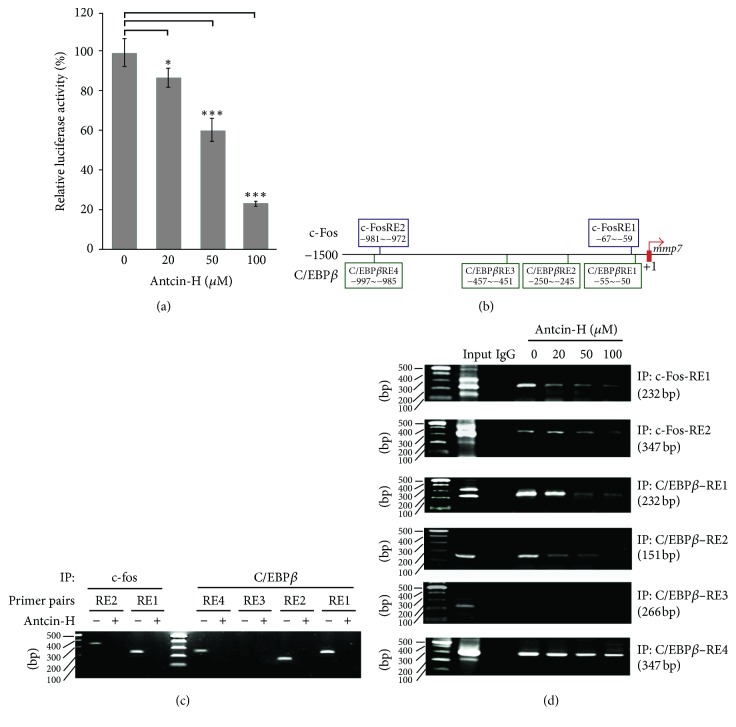
Figure 6
Inhibition of c-Fos and C/EBP-β…
Figure 6
Inhibition of c-Fos and C/EBP-β activities involved in antcin-H-mediated MMP-7 downregulation. (a) Reporter…
Figure 6 Inhibition of c-Fos and C/EBP-β activities involved in antcin-H-mediated MMP-7 downregulation. (a) Reporter luciferase assay. 786-0 cells were transiently transfected with reporter vector containing MMP-7 promoter +1~−1500 region or control vector for 24 h, and then the cells were treated without or with 20, 50, and 100 μM antcin-H for another 24 h. After incubation, the luciferase activity was measured and the relative luciferase activity was presented as means ± SD. Statistically significant, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. (b) Putative binding sites of c-Fos and C/EBP-β located at upstream of MMP-7 promoter. (c) Antcin-H prevents c-Fos and C/EBP-β binding to the MMP-7 upstream promoter/response element region. The 786-0 cells were treated without or with 100 μM antcin-H for 24 h, the cells were collected, and then ChIP assay was carried out. (d) Antcin-H dose-dependently inhibits c-Fos and C/EBP-β binding to the MMP-7 upstream promoter/response element region. The 786-0 cells were treated without or with 20, 50, and 100 μM antcin-H for 24 h, the cells were collected, and then the activity of c-Fos and C/EBP-β binding to each response site located at MMP-7 promoter upstream was determined by ChIP assay.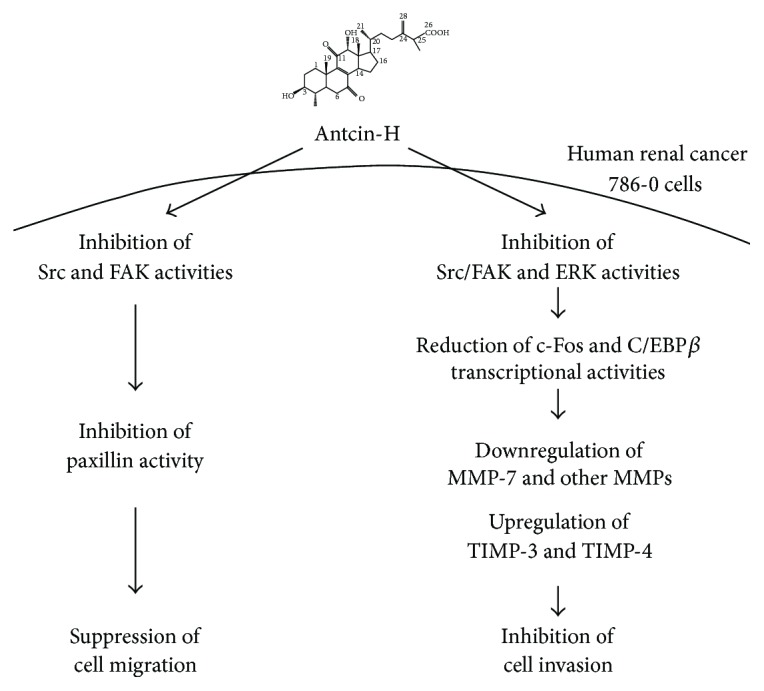
Figure 7
Schematic model of the proposed…
Figure 7
Schematic model of the proposed signaling pathways involved in suppressing cell migration and…
Figure 7 Schematic model of the proposed signaling pathways involved in suppressing cell migration and invasion by antcin-H in human RCC 786-0 cells. Antcin-H inhibits Src, FAK, and ERK1/2 phosphorylated activation, in turn decreasing paxillin, c-Fos, and C/EBP-β activities, reducing the binding of c-Fos and phosphorylated-C/EBP-β to AP-1 and C/EBP-β response elements, thereby decreasing MMPs gene expression, especially MMP-7. Downregulation of MMP-7 and upregulation of TIMP-3 and TIMP-4 gene expression block the degradation of the extracellular matrix proteins and impair the cell invasion. Besides, reducing paxillin phosphorylation and vimentin expression prevents 786-0 cell motility. All figures (7)