Antrodia Cinnamomea Reduces Carbon Tetrachloride-induced Hepatotoxicity In Male Wister Rats
Abstract
Figures 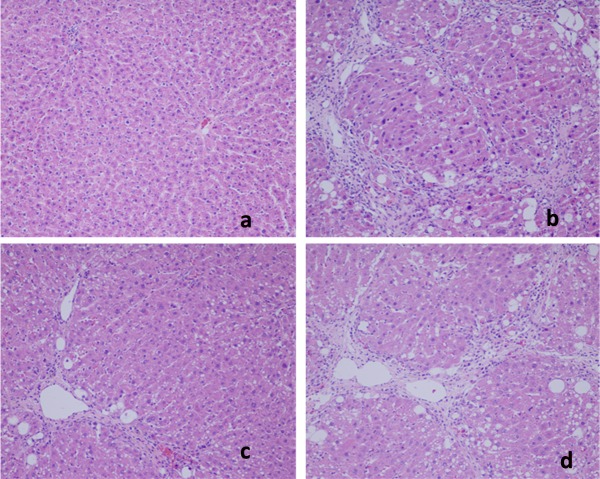
Figure 1. Microphotograph of rat liver (H&E…
Figure 1. Microphotograph of rat liver (H&E stain). (a) Representative section of liver from the…
Figure 1. Microphotograph of rat liver (H&E stain). (a) Representative section of liver from the control group showing normal histology. Normal hepatic cells are characterized by well-defined cell linings, prominent nucleus, and prominent central vein surrounded by reticular fibers. (b) Massive necrosis formation, hepatocytes ballooning, distortion of hepatocytes, shrinkage of nucleus, clear cell foci formation, loss of cellular boundaries, and reticular fibers were observed in CCl4-intoxicated rat liver section thus indicative of extensive liver injuries. (c) High-dose treatment of Antrodia cinnamomea partly prevented hepatoprotective activity. The histopathological changes such as necrosis, ballooning, clear cell foci formation, and structural loss of hepatic lobules were moderate recovery. (d) However, the histological architecture of liver sections of the rats treated with silymarin still showed some cavities and necrosis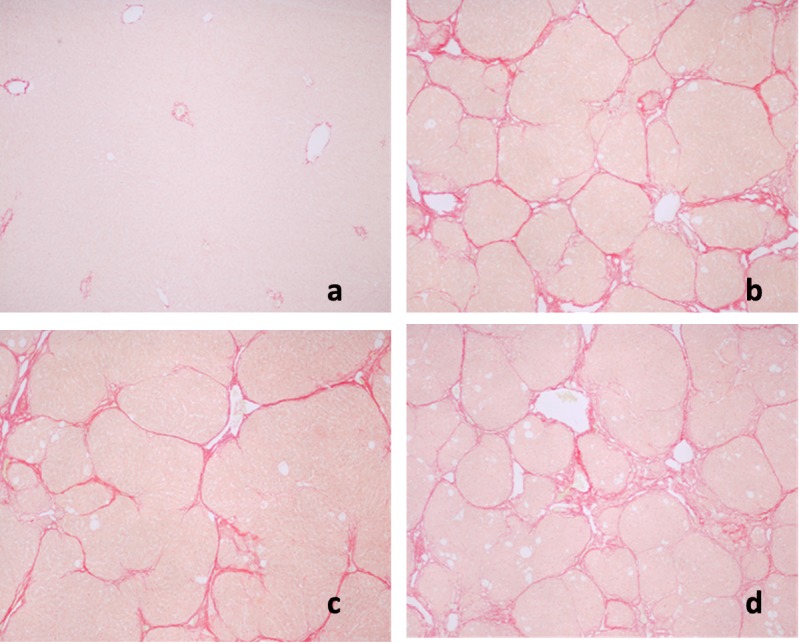
Figure 2. Sirius red staining of rat…
Figure 2. Sirius red staining of rat liver sections. a: Control; b: CCl4 + H2O,…
Figure 2. Sirius red staining of rat liver sections. a: Control; b: CCl4 + H2O, showing micronodular formation and complete septa interconnection with each other; c: CCl4 + high-dose treatment of Antrodia cinnamomea; d: CCl4 + silymarin.