Antcin K inhibits VCAM-1-dependent monocyte adhesion in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts
Abstract
Figures 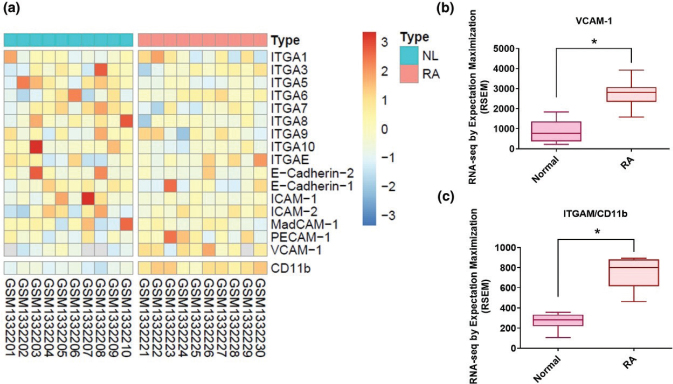
Fig. 1
Levels of cell adhesion molecule…
Fig. 1
Levels of cell adhesion molecule expression in RA synovial tissue. (a) Records downloaded…
Fig. 1 Levels of cell adhesion molecule expression in RA synovial tissue. (a) Records downloaded from the GEO database (accession code: GDS5401) were screened for protein expression markers of the four main CAM classes (cadherins, integrins, selectins, and CAMs of the immunoglobulin superfamily) in synovial tissue samples from 10 patients with RA and 10 healthy individuals (b, c). Levels of VCAM-1 and CD11b expressions in RA and normal synovial tissues. RA, rheumatoid arthritis; NL, normal controls. *P < 0.05 compared with normal controls.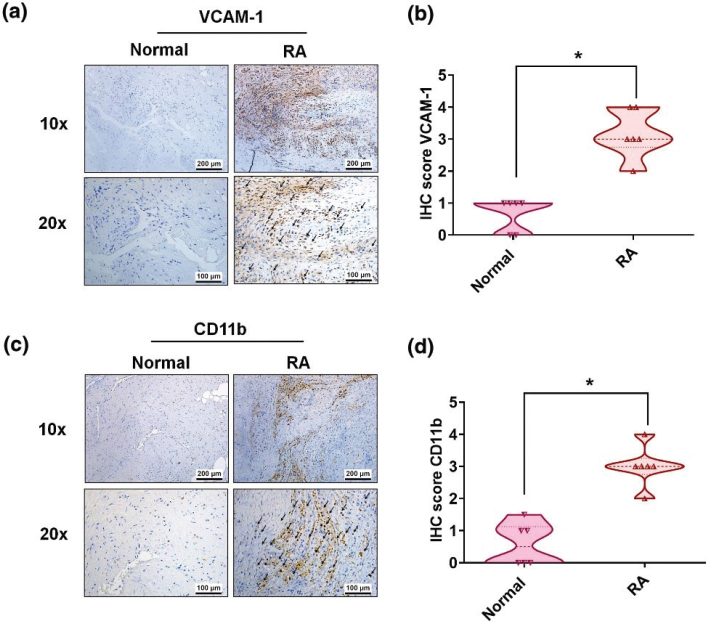
Fig. 2
Upregulation of VCAM-1 and CD11b…
Fig. 2
Upregulation of VCAM-1 and CD11b expressions in human RA synovial tissue. (a) Immunostaining…
Fig. 2 Upregulation of VCAM-1 and CD11b expressions in human RA synovial tissue. (a) Immunostaining of VCAM-1 expression in human RA (n = 6) and normal tissue (n = 6). Black arrows indicate levels of VCAM-1 expression in the synovial tissue. (b) Quantification of VCAM-1 expression by IHC score. (c) IHC staining of CD11b expression in RA (n = 6) and normal tissue (n = 6). Black arrows indicate levels of CD11b expression in the synovial tissue. (d) Quantification of CD11b expression by IHC score. RA, rheumatoid arthritis; NL, normal controls. *P < 0.05 compared with normal controls.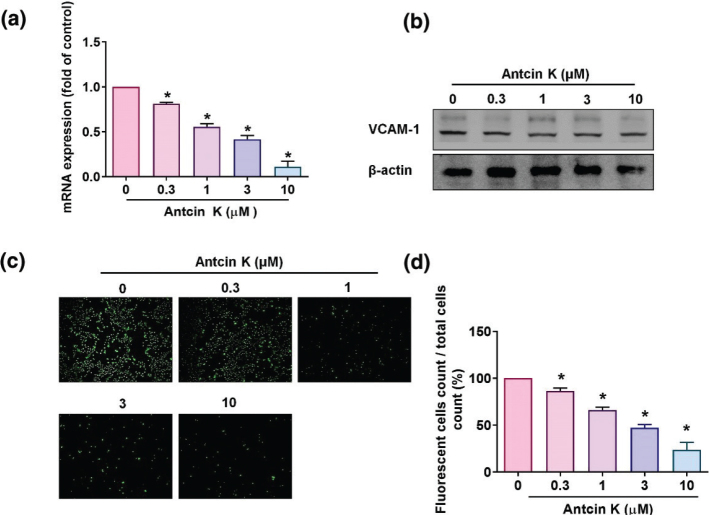
Fig. 3
Antcin K inhibits VCAM-1 expression…
Fig. 3
Antcin K inhibits VCAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion in human RASFs. (a, b)…
Fig. 3 Antcin K inhibits VCAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion in human RASFs. (a, b) Antcin K (0.3–10 μM) was administered to RASFs for 24 h, and then VCAM-1 expression was examined using RT-qPCR (n = 4) and Western blot analyses (n = 3). (c, d) RASFs were incubated with indicated concentrations of Antcin K for 24 h. BCECF-AM-labeled THP-1 cells were then added to the RASFs for 1 h. Monocyte adherence in cultured RASFs was examined by fluorescence microscopy and photographed (n = 4). *P < 0.05 compared with the control.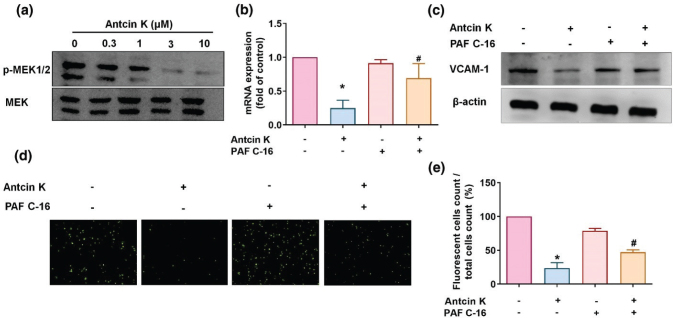
Fig. 4
The MEK1/2 pathway is involved…
Fig. 4
The MEK1/2 pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced VCAM-1 inhibition. (a) Antcin K…
Fig. 4 The MEK1/2 pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced VCAM-1 inhibition. (a) Antcin K (0.3–10 μM) was administered to RASFs, and MEK1/2 phosphorylation was analyzed by Western blot analysis (n = 3). (b–e) RASFs were stimulated with the MEK activator (PAF C-16) for 30 min and then incubated with 10 μM of Antcin K for 24 h. VCAM-1 levels were analyzed by RT-qPCR (n = 4) and Western blot (n = 3). Monocyte adhesion in cultured RASFs was determined by the monocyte adhesion assay (n = 4). *P < 0.05 compared with the control; #P < 0.05 compared with Antcin K treatment.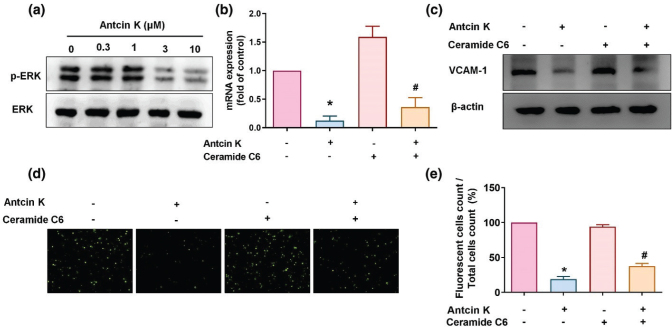
Fig. 5
The ERK pathway is involved…
Fig. 5
The ERK pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced VCAM-1 inhibition. (a) RASFs were…
Fig. 5 The ERK pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced VCAM-1 inhibition. (a) RASFs were treated with Antcin K (0.3–10 μM) for 24 h, and then ERK phosphorylation was examined by Western blot (n = 3). (b–e) RASFs were stimulated with the ERK activator (ceramide C6) for 30 min and then incubated with 10 μM of Antcin K for 24 h. VCAM-1 levels were analyzed by RT-qPCR (n = 4) and Western blot (n = 3). Monocyte adhesion in cultured RASFs was determined by the monocyte adhesion assay (n = 4). *P < 0.05 compared with the control; #P < 0.05 compared with Antcin K treatment.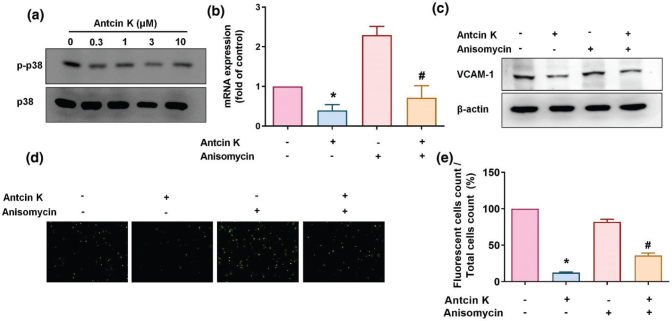
Fig. 6
The p38 pathway is involved…
Fig. 6
The p38 pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced VCAM-1 inhibition. (a) RASFs were…
Fig. 6 The p38 pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced VCAM-1 inhibition. (a) RASFs were treated with Antcin K (0.3–10 μM) for 24 h, and then p38 phosphorylation was examined by Western blot (n = 3). (b–e) RASFs were stimulated with the p38 activator (anisomycin) for 30 min and then incubated with Antcin K (10 μM) for 24 h. VCAM-1 levels were examined by RT-qPCR (n = 4) and Western blot (n = 3). Monocyte adhesion in cultured RASFs was examined by the monocyte adhesion assay (n = 4). *P < 0.05 compared with the control; #P < 0.05 compared with Antcin K treatment.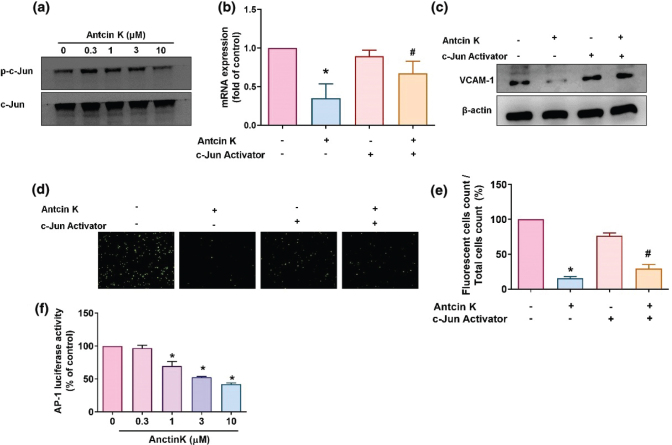
Fig. 7
The AP-1 pathway is involved…
Fig. 7
The AP-1 pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced VCAM-1 inhibition. (a) RASFs were…
Fig. 7 The AP-1 pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced VCAM-1 inhibition. (a) RASFs were treated with Antcin K (0.3–10 μM) for 24 h, and then c-Jun phosphorylation was examined by Western blot (n = 3). (b–e) RASFs were stimulated with the AP-1 activator (D-erythro-SPC) for 30 min and then incubated with Antcin K (10 μM) for 24 h. VCAM-1 levels were examined by RT-qPCR (n = 4) and Western blot (n = 3). Monocyte adhesion in cultured RASFs was examined by the monocyte adhesion assay (n = 4). (f) RASFs were transfected with the AP-1 luciferase plasmid and then treated with Antcin K at the indicated concentrations, and luciferase activity was quantified. *P < 0.05 compared with the control; #P < 0.05 compared with Antcin K treatment.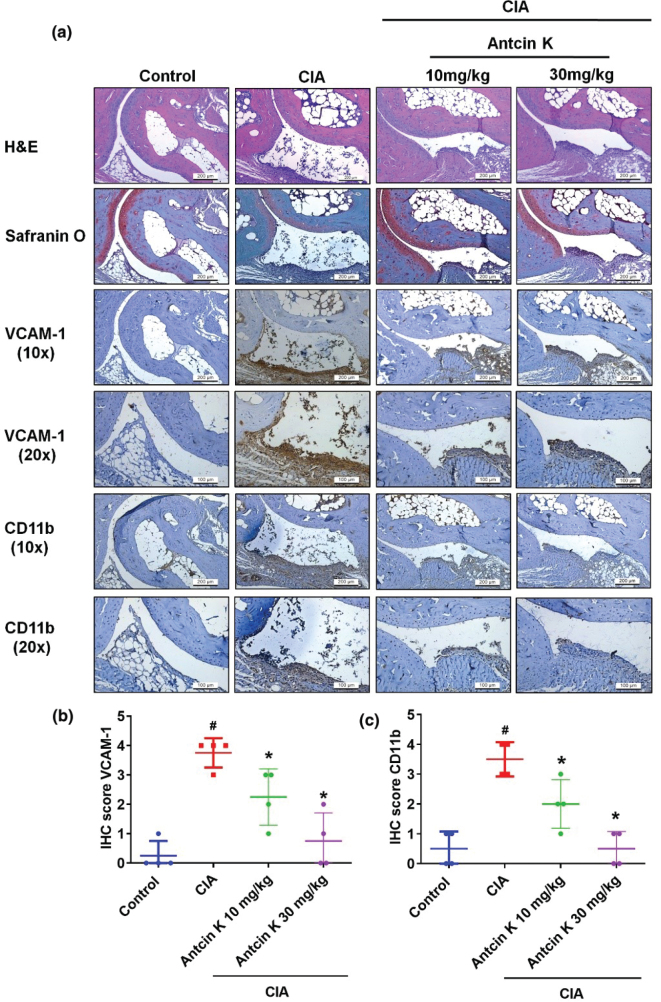
Fig. 8
Antcin K reduces histological severity…
Fig. 8
Antcin K reduces histological severity of RA disease. (a) Specimens from control ankle…
Fig. 8 Antcin K reduces histological severity of RA disease. (a) Specimens from control ankle joints, CIA ankle joints, and Antcin K-treated CIA ankle joints were counterstained with H&E and Safranin-O and then immunostained with VCAM-1 and CD11b antibodies (n = 4). (b–c) Quantification of VCAM-1 and CD11b expressions by IHC score (n = 4). #P < 0.05 compared with controls; *P < 0.05 compared with untreated CIA mice.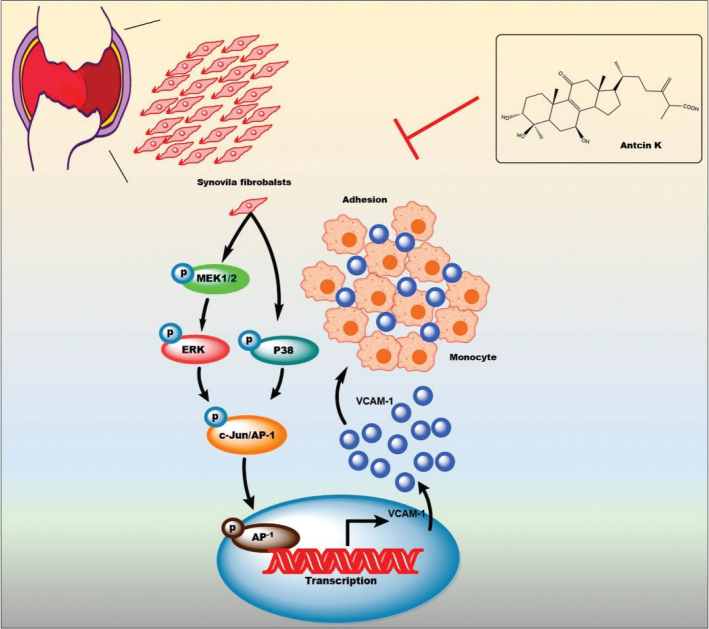
Fig. 9
The schema illustrates how the…
Fig. 9
The schema illustrates how the antiarthritic mechanisms of Antcin K are achieved through…
Fig. 9 The schema illustrates how the antiarthritic mechanisms of Antcin K are achieved through the inhibition of VCAM-1 via the MEK1/2-ERK, p38, and AP-1 signaling pathways. All figures (9)