Antcin K Inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 Expression in Synovial Fibroblasts and Ameliorates Cartilage Degradation: Implications for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Extracts from Taiwan's traditional medicinal mushroom, Antrodia cinnamomea, exhibit anti-inflammatory activities in cellular and preclinical studies. However, this paper is the first to report that Antcin K, a triterpenoid isolated from A. cinnamomea, inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts (RASFs), which are major players in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease. In our analysis of the mechanism of action, Antcin K inhibited the expression of three cytokines (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α], interleukin 1 beta [IL-1β] and IL-8) in human RASFs; cytokines that are crucial to RA synovial inflammation. Notably, incubation of RASFs with Antcin K reduced the phosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase (FAK), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (AKT) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling cascades, all of which promote cytokine production in RA. Intraperitoneal injections of Antcin K (10 mg/kg or 30 mg/kg) attenuated paw swelling, cartilage degradation and bone erosion, and decreased serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-8 in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice; in further experiments, IL-6 levels were similarly reduced. The inhibitory effects of Antcin K upon TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 expression in human RASFs was achieved through the downregulation of the FAK, PI3K, AKT and NF-κB signaling cascades. Our data support clinical investigations using Antcin K in RA disease.
Figures 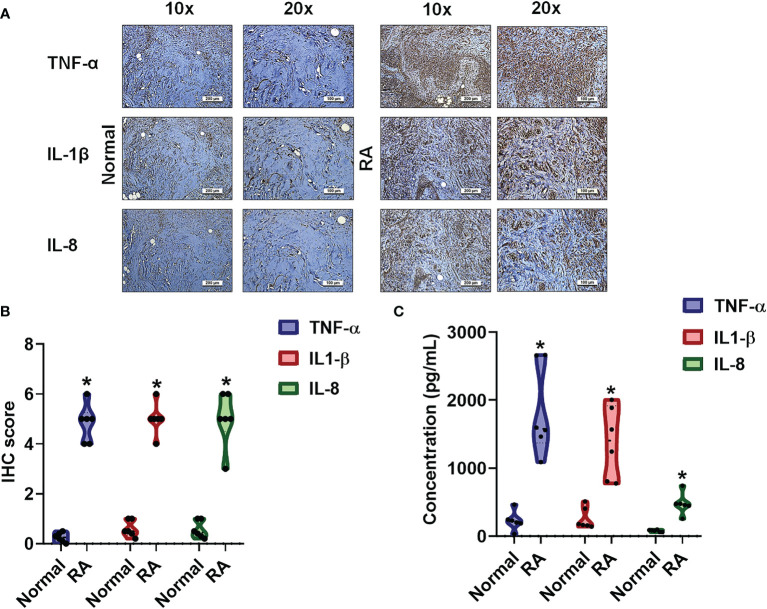
Figure 1
The identification of cytokines that…
Figure 1
The identification of cytokines that interfere with RA severity. (A, B) RA and…
Figure 1 The identification of cytokines that interfere with RA severity. (A, B) RA and normal synovial tissue specimens were analyzed by IHC. (C) Cytokine plasma levels were upregulated in RA patients. ELISA assessments of blood samples (N=6) from RA patients and healthy volunteers determined levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with controls.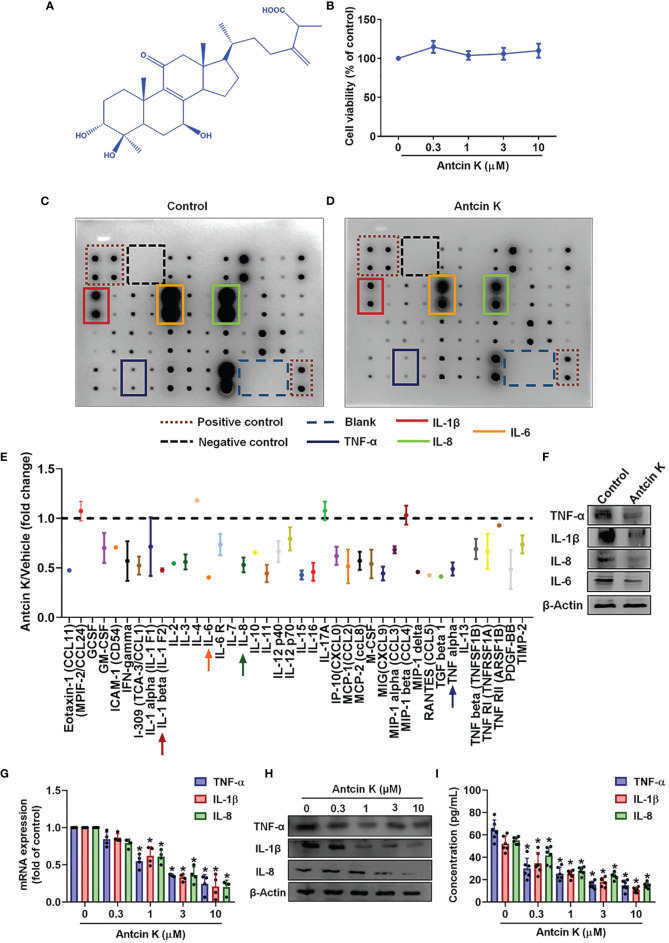
Figure 2
Antcin K inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β…
Figure 2
Antcin K inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 expression in RASFs. (A) Chemical structure…
Figure 2 Antcin K inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 expression in RASFs. (A) Chemical structure of compound Antcin K. (B) Cells were incubated with Antcin K (0.3, 1, 3 or 10 μM for 24 and cell viability was examined by the MTT assay. (C–E) Cells were incubated with Antcin K (10 μM) for 24 h and the expression of 40 inflammatory factors was quantified by a human inflammation antibody array. (F) Inhibitory effects of Antcin K on TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and protein secretion were evaluated by Western blot. (G–I) Cells were incubated with Antcin K (0.3, 1, 3 or 10 μM) for 24 h. TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 mRNA expression and protein secretion were evaluated by qPCR, Western blot, and ELISA. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with controls.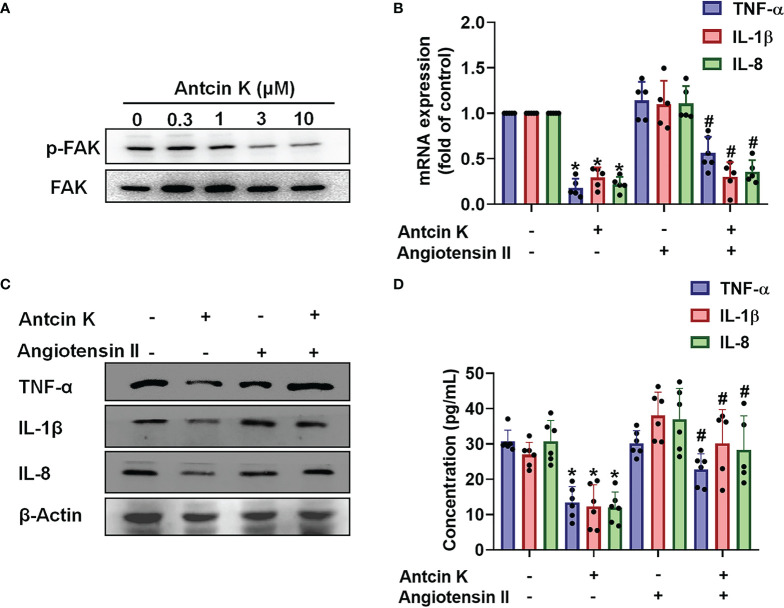
Figure 3
The FAK pathway is involved…
Figure 3
The FAK pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β and…
Figure 3 The FAK pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 production in RASFs. (A) Cells were treated with Antcin K (0.3, 1, 3 or 10 μM) for 24 h and FAK phosphorylation was examined by Western blot. (B–D) Cells were pretreated with the FAK activator Angiotensin II for 30 min, then treated with Antcin K (10 μM) for 24 h. TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 mRNA expression and protein secretion were examined by qPCR, Western blot and ELISA. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with controls; #P < 0.05 compared with the Antcin K-treated group.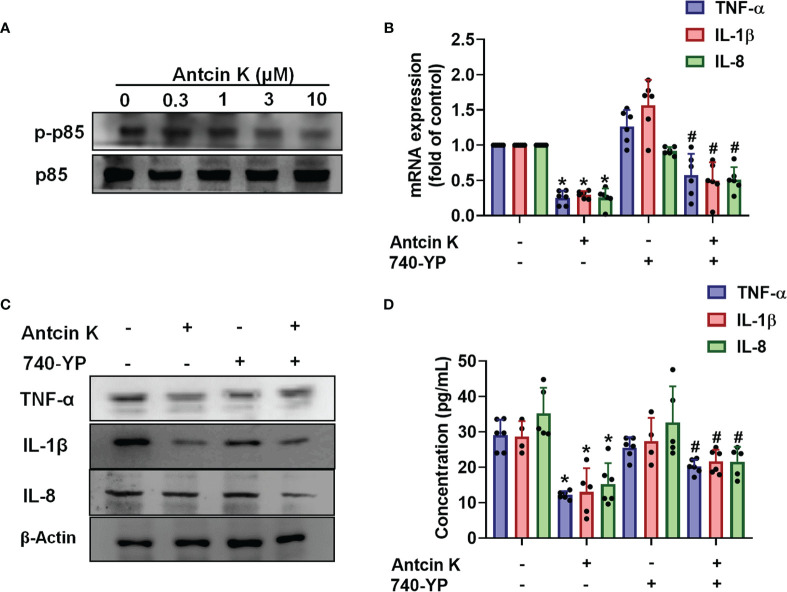
Figure 4
The PI3K pathway is involved…
Figure 4
The PI3K pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β and…
Figure 4 The PI3K pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 production in RASFs. (A) Cells were treated with Antcin K (0.3, 1, 3 or 10 μM) for 24 h and PI3K phosphorylation was examined by Western blot. (B–D) Cells were pretreated with PI3K activator 740-YP for 30 min, then treated with Antcin K (10 μM) for 24 h. TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 mRNA expression and protein secretion were examined by qPCR, Western blot and ELISA. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with controls; #P < 0.05 compared with the Antcin K-treated group.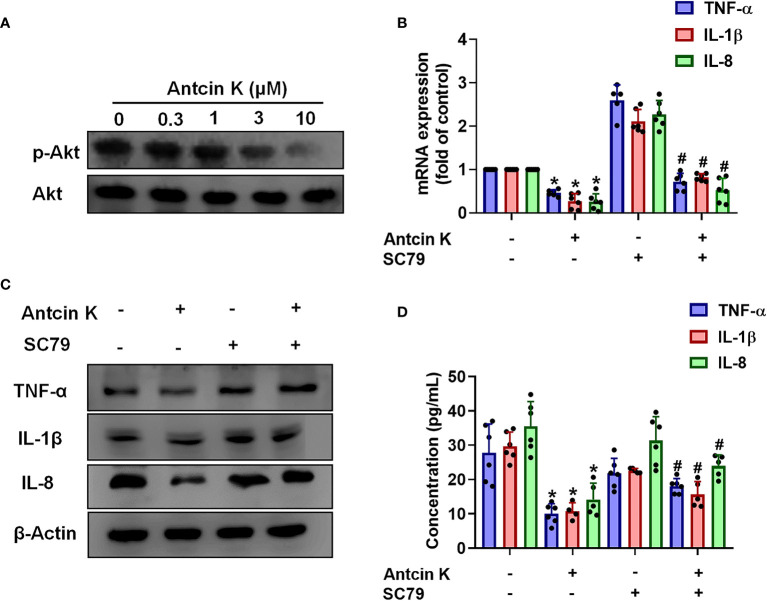
Figure 5
The AKT pathway is involved…
Figure 5
The AKT pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β and…
Figure 5 The AKT pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 production in synovial fibroblasts. (A) Cells were treated with Antcin K (0.3, 1, 3, or 10 μM) for 24 h and AKT phosphorylation was examined by Western blot. Cells were pretreated with an AKT activator (SC-79) for 30 min, then treated with Antcin K (10 μM) for 24 h. (B–D) TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 mRNA expression and protein secretion were examined by qPCR, Western blot and ELISA. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with controls; #P < 0.05 compared with the Antcin K-treated group.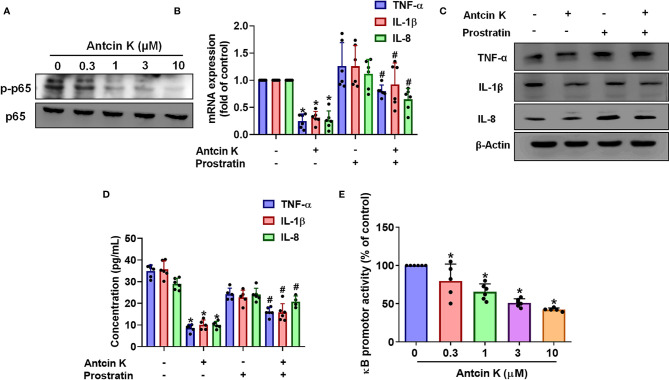
Figure 6
The NF-κB pathway is involved…
Figure 6
The NF-κB pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β and…
Figure 6 The NF-κB pathway is involved in Antcin K-induced inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 production in RASFs. (A) Cells were treated with Antcin K (0.3, 1, 3 or 10 μM) for 24 h and NF-κB phosphorylation was examined by Western blot. Cells were pretreated with the NF-κB activator (prostratin) for 30 min, then treated with Antcin K (10 μM) for 24 h. (B–D) TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 mRNA expression and protein secretion were examined by qPCR, Western blot and ELISA. (E) Cells were transfected with the NF-κB luciferase plasmid, then incubated with Antcin K (0.3, 1, 3, or 10 μM) for 24 h and luciferase activity was determined. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with controls; #P < 0.05 compared with the Antcin K-treated group.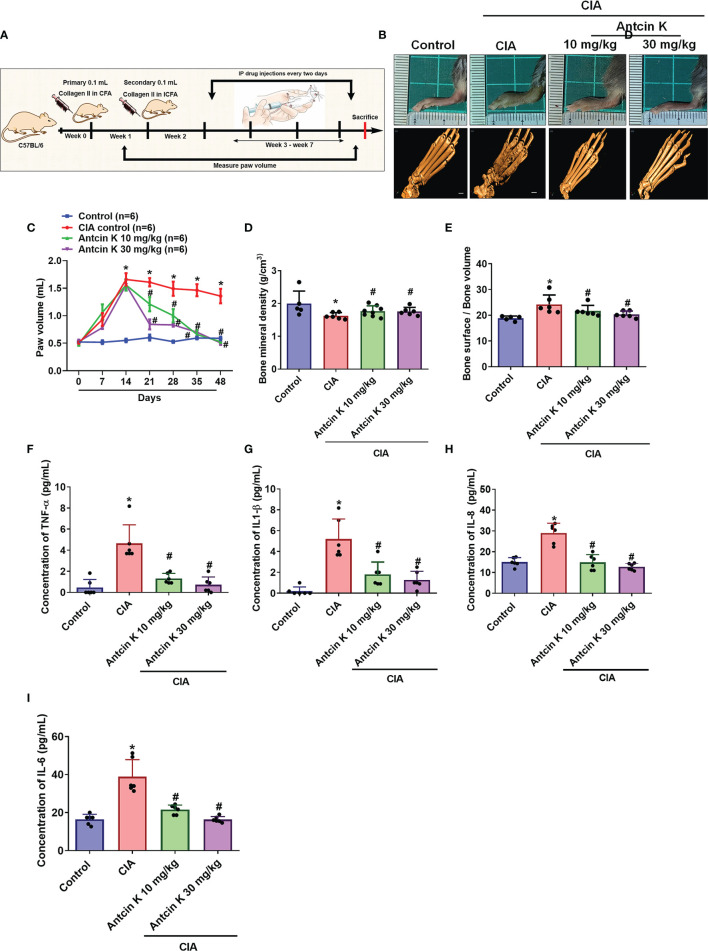
Figure 7
Antcin K ameliorated paw swelling…
Figure 7
Antcin K ameliorated paw swelling and cartilage degradation in CIA mice. (A) Workflow…
Figure 7 Antcin K ameliorated paw swelling and cartilage degradation in CIA mice. (A) Workflow of CIA induction and Antcin K injections. (B, C) Hind paw swelling was photographed and measured with a digital plethysmometer in healthy controls, untreated CIA mice, and in CIA mice administered Antcin K 10 mg/kg or 30 mg/kg for 48 weeks. Representative micro-CT images of the hind paws were recorded on Day 48. (D, E) Quantifications of bone volume, bone surface, and bone density. (F–I) Serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 were analyzed by ELISA. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with controls; #P < 0.05 compared with the untreated CIA mice.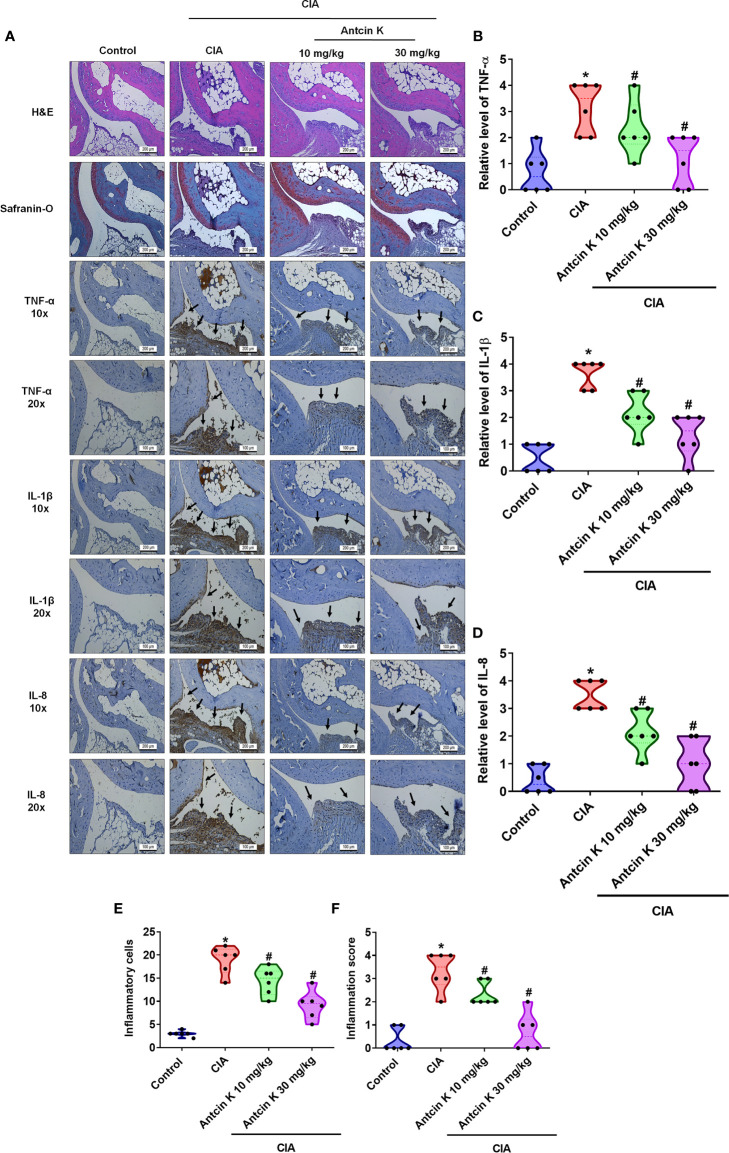
Figure 8
Effects of Antcin K quantified…
Figure 8
Effects of Antcin K quantified by histopathological changes in ankle joints from CIA…
Figure 8 Effects of Antcin K quantified by histopathological changes in ankle joints from CIA mice. (A) Representative magnified images of histologic sections taken from ankle joints that were stained with H&E and Safranin-O, and IHC staining for TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 antibodies from healthy controls, untreated CIA mice, and CIA mice administered Antcin K 10 mg/kg or 30 mg/kg (N=6 per group). (B–D) Quantification of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 expression by IHC score. (E, F) Quantification of inflammation scores and pathology findings in ankle joint synovium and adjacent tissue (details are provided in Supplementary Table 1). Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with controls; #P < 0.05 compared with the untreated CIA mice.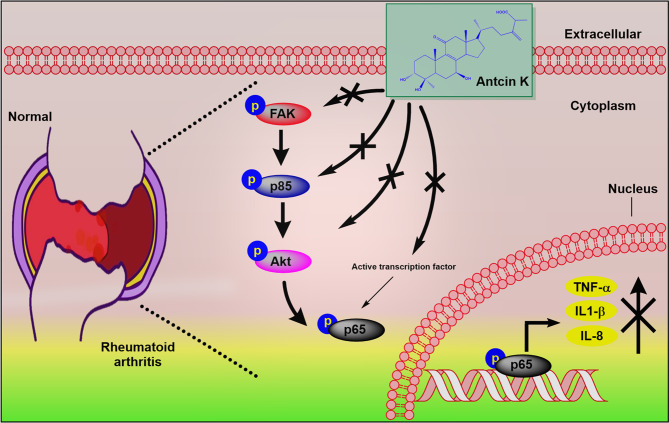
Figure 9
Schematic diagram summarizes the mechanism…
Figure 9
Schematic diagram summarizes the mechanism whereby Antcin K inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production. Antcin…
Figure 9 Schematic diagram summarizes the mechanism whereby Antcin K inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production. Antcin K inhibits TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8 production in human RA synovial fibroblasts and in serum and synovial tissue from CIA mice. These anti-inflammatory effects occur through the FAK/PI3K, AKT, and NF-κB signaling cascades. All figures (9)