The Disruption of the β-Catenin/TCF-1/STAT3 Signaling Axis by 4-Acetylantroquinonol B Inhibits the Tumorigenesis and Cancer Stem-Cell-Like Properties of Glioblastoma Cells, In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
Figures 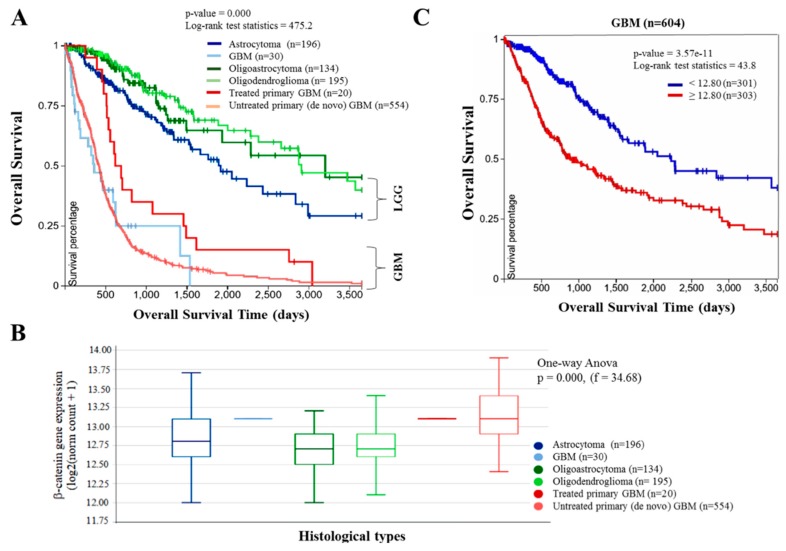
Figure 1
Aberrant expression of β-catenin is…
Figure 1
Aberrant expression of β-catenin is characteristic of glioblastoma (GBM) and correlates with poor…
Figure 1 Aberrant expression of β-catenin is characteristic of glioblastoma (GBM) and correlates with poor prognosis. (A) Kaplan–Meier plot showing the overall survival of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) lower grade glioma and glioblastoma cohort (Glioma (GBMLGG), n = 1152) according to their histological type. (B) β-catenin expression across the different histological type of glioma and glioblastoma in the TCGA GBMLGG cohort. (C) Kaplan–Meier plot based on the β-catenin expression level in only the glioblastoma component of the TCGA GBMLGG dataset using the gene expression RNAseq-illuminaHiSeq. Expression cutoff is based on median expression. LGG, low grade glioma; GBM, glioblastoma.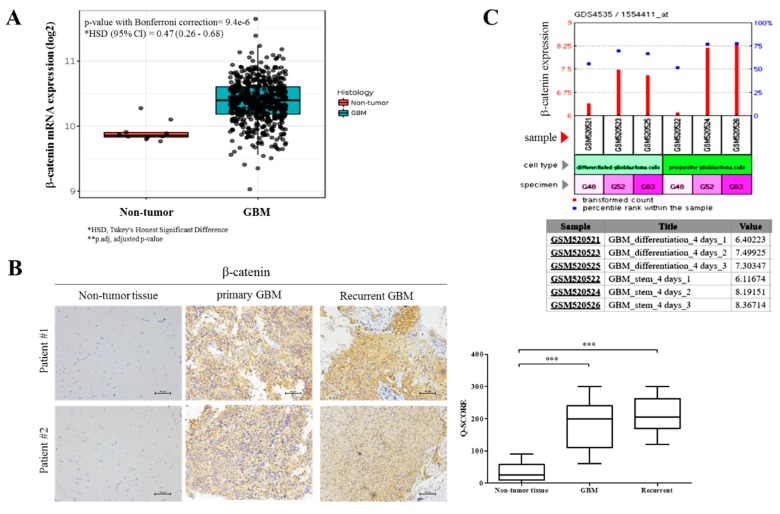
Figure 2
β-catenin facilitates GBM oncogenicity and…
Figure 2
β-catenin facilitates GBM oncogenicity and disease recurrence, as well as their cancer stem…
Figure 2 β-catenin facilitates GBM oncogenicity and disease recurrence, as well as their cancer stem cell-like traits. (A) TCGA brain dataset (n = 557) using the Human Genome U133A Array showing the differential β-catenin mRNA expression in GBM (n = 547) and normal brain (n = 10) samples. (B) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining comparing expression of β-catenin in GBM, recurrent and adjacent non-tumor brain tissues in 2 Taipei Medical University Shuang Ho Hospital (TMU-SHH) brain tumor patients. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; GBM, glioblastoma. Scale bar: 50 μm (C) GEO dataset GSE20736/GPL570/GDS4535 shows time-dependent enhancement of β-catenin expression levels in human progenitor GBM cells compared to their differentiated counterparts.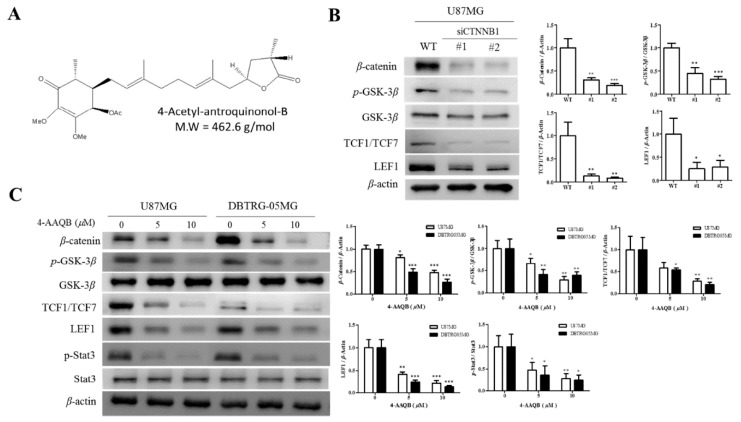
Figure 3
4-AAQB disrupts β-catenin/TCF-1/Stat3 signaling axis…
Figure 3
4-AAQB disrupts β-catenin/TCF-1/Stat3 signaling axis in GBM cells. ( A ) Chemical structure…
Figure 3 4-AAQB disrupts β-catenin/TCF-1/Stat3 signaling axis in GBM cells. (A) Chemical structure of 4-Acetylantroquinonol B; C26H38O7, 462.58 g/mol. Representative Western blot data and graphical quantification showing (B) the knock-down efficiency of β-catenin in human GBM cell line U87MG, with corresponding effect on the expression levels of pGSK3β, GSK-3β, TCF1/TCF7, and LEF1 proteins; and (C) the dose-dependent downregulation of β-catenin, pGSK3β, TCF1/TCF7, LEF1, and p-Stat3 proteins in U87MG and DBTRG05MG cells treated with increasing concentrations of 4-AAQB for 24 h. β-actin served as loading control. siCTNNB1, short interfering RNA directed specifically against β-catenin; WT, wild type; * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001. All data is representative of experiments performed 4 times in triplicates.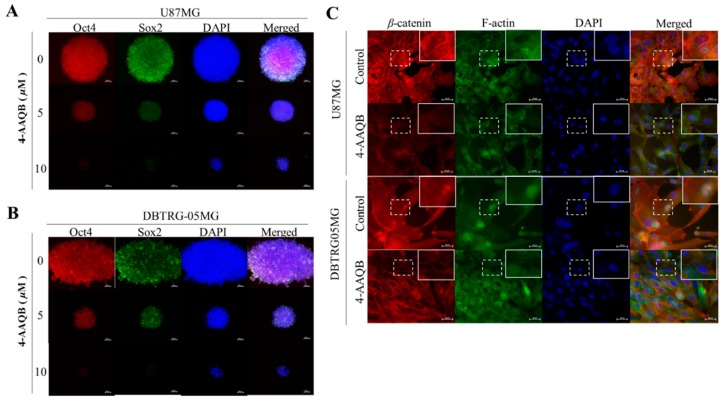
Figure 4
4-AAQB inhibits the nuclear localization…
Figure 4
4-AAQB inhibits the nuclear localization of β-catenin, Sox2, and Oct4 in GBM cells.…
Figure 4 4-AAQB inhibits the nuclear localization of β-catenin, Sox2, and Oct4 in GBM cells. U87MG and DBTRG-05MG cells treated with or without 5–10 μM 4-AAQB were immunostained with Sox2 (green), Oct4 (red), β-catenin (red), and F-actin (green) antibodies, then image visualization and analysis carried out by fluorescence microscopy. Treatment with 5 or 10 μM 4-AAQB markedly decreased nuclear Sox2 and Oct4 protein expression in (A) U87MG or (B) DBTRG-05MG cells. (C) Immunohistochemistry show reduced nuclear expression of β-catenin and F-actin after treatment with 10 μM 4-AAQB. Original magnification ×200. DAPI (blue) served as nuclear marker.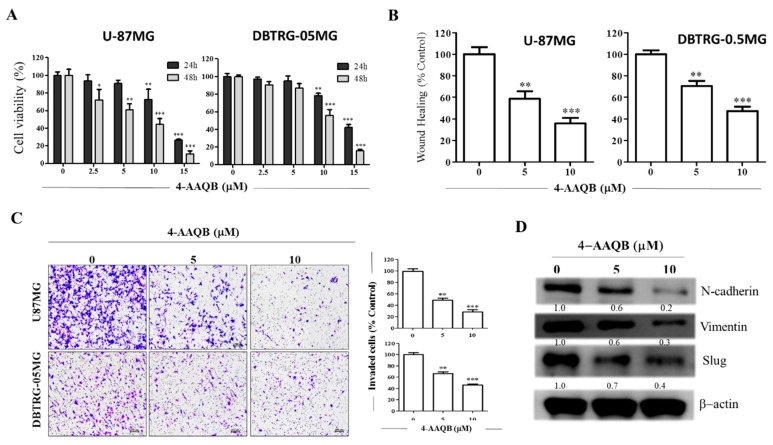
Figure 5
4-AAQB significantly suppresses the viability…
Figure 5
4-AAQB significantly suppresses the viability and oncogenicity of GBM cells. ( A )…
Figure 5 4-AAQB significantly suppresses the viability and oncogenicity of GBM cells. (A) The dose-dependent cytotoxic effect of 4-AAQB on the cell viability of U-87MG and DBTRG-05MG. (B) Representative photo-images and graphical quantification showing the effect of 5 μM and 10 μM of 4-AAQB on the migration of U-87MG and DBTRG-05MG over 24 h duration. (C) 4-AAQB dose-dependently inhibit the number of invaded U-87MG and DBTRG-05MG cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) The inhibitory effect of 5 M and 10 M 4-AAQB on the expression levels of β-catenin, vimentin, and slug proteins in DBTRG-05MG cells as shown by Western blot assay. β-actin served as loading control. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; All data is representative of experiments performed 4 times in triplicates.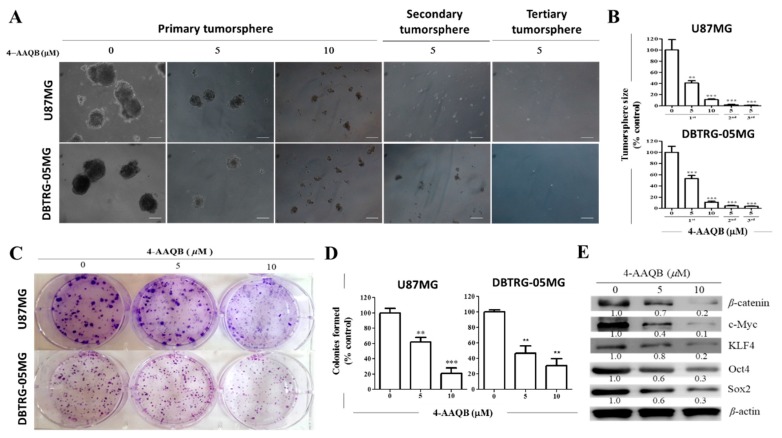
Figure 6
4-AAQB markedly inhibits the stem…
Figure 6
4-AAQB markedly inhibits the stem cell-like phenotype of U87MG and DBTRG-05MG cells. (…
Figure 6 4-AAQB markedly inhibits the stem cell-like phenotype of U87MG and DBTRG-05MG cells. (A) Representative photo-images and (B) graphical quantification showing 4-AAQB significantly reduce the size and number of U87MG and DBTRG-05MG primary, secondary, and tertiary generation tumorspheres formed. Original magnification = 200×. (C) Representative photo-images and (D) graphical representations of 4-AAQB effect on the ability of U87MG and DBTRG-05MG cells to form colonies; (E) The dose-dependent inhibitory effect of 5–10 M 4-AAQB treatment on the expression levels of β-catenin, c-Myc, KLF4, Oct4, and Sox2 proteins in DBTRG05MG cells shown in a representative Western blot data. β-actin served as loading control. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; All data is representative of experiments performed 4 times in triplicates.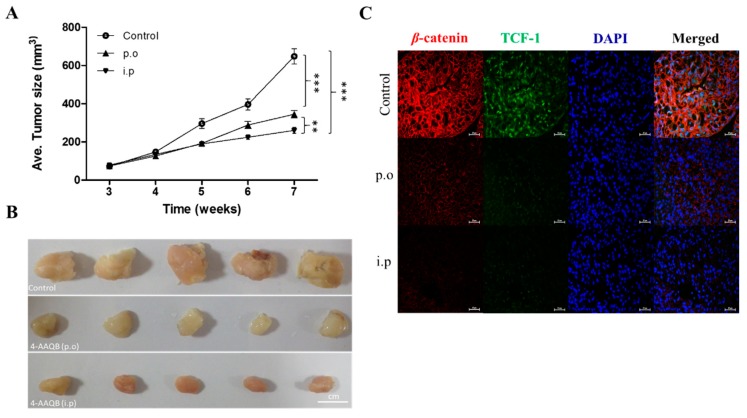
Figure 7
Compared to oral gavage, intraperitoneal…
Figure 7
Compared to oral gavage, intraperitoneal 4-AAQB significantly and more efficiently suppresses GBM stem…
Figure 7 Compared to oral gavage, intraperitoneal 4-AAQB significantly and more efficiently suppresses GBM stem cell-induced tumor growth, in vivo. (A) Tumor size vs time curve show the inhibitory effect of 4-AAQB on U87MG tumor growth either via p.o or i.p route, as compared to the control group. (B) Photographs of tumor samples harvested from the in vivo studies. (C) The differential effects of oral and intraperitoneal administration of 4-AAQB on the expression and localization of TCF-1 and β-catenin in xenograft-derived GBM primary culture. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; 4′, 6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) served as nuclear marker. All figures (7)