Review of Bioactivity, Isolation, and Identification of Active Compounds from Antrodia cinnamomea
Abstract
Antrodia cinnamomea is a precious and popular edible and medicinal mushroom. It has attracted increasing attention due to its various and excellent bioactivities, such as hepatoprotection, hypoglycemic, antioxidant, antitumor, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulation, and gut microbiota regulation properties. To elucidate its bioactivities and develop novel functional foods or medicines, numerous studies have focused on the isolation and identification of the bioactive compounds of A. cinnamomea. In this review, the recent advances in bioactivity, isolation, purification, and identification methods of active compounds from A. cinnamomea were summarized. The present work is beneficial to the further isolation and discovery of new active compounds from A. cinnamomea.
Figures 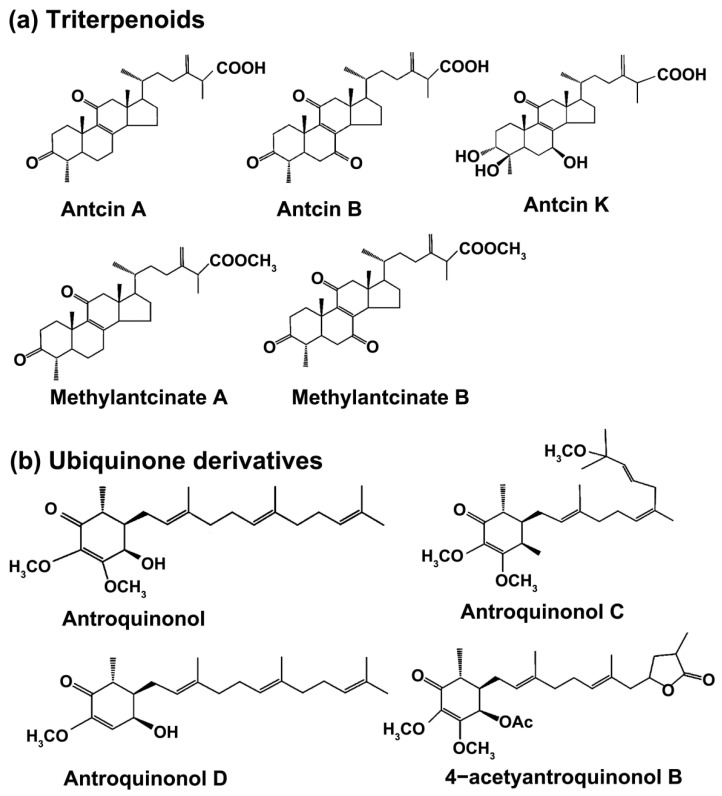
Figure 1
The chemical structures of the…
Figure 1
The chemical structures of the main bioactive components from Antrodia cinnamomea . (…
Figure 1 The chemical structures of the main bioactive components from Antrodia cinnamomea. (a) Triterpenoids, (b) ubiquinone derivatives, (c) maleic and succinic acid derivatives, (d) benzene derivatives.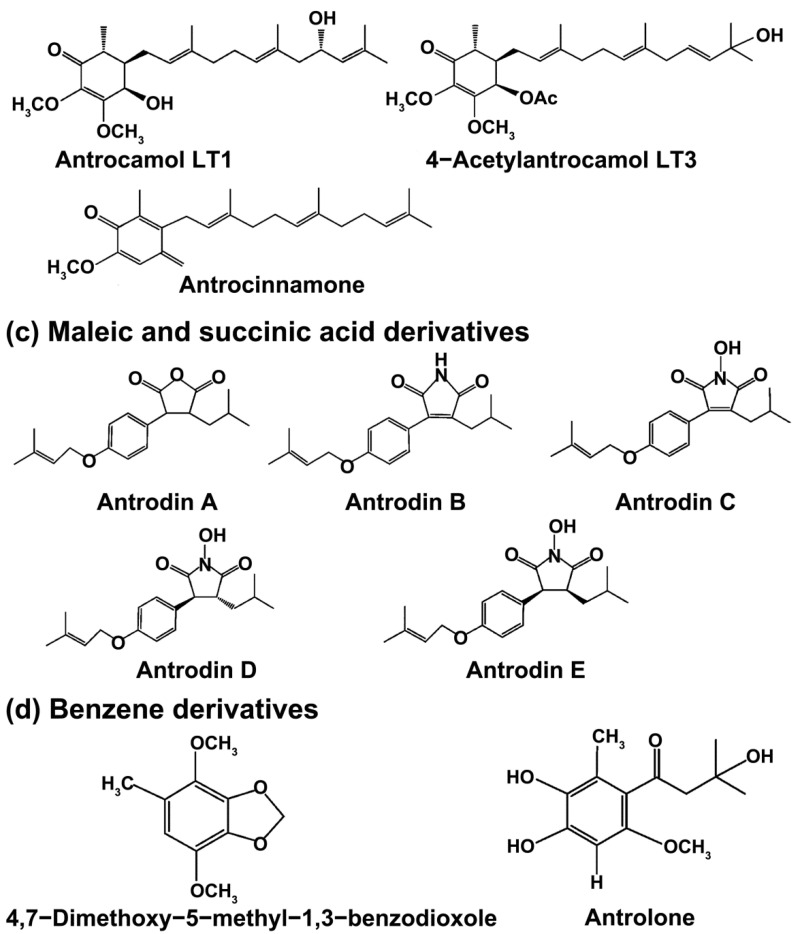
Figure 1
The chemical structures of the…
Figure 1
The chemical structures of the main bioactive components from Antrodia cinnamomea . (…
Figure 1 The chemical structures of the main bioactive components from Antrodia cinnamomea. (a) Triterpenoids, (b) ubiquinone derivatives, (c) maleic and succinic acid derivatives, (d) benzene derivatives.