Optimization of Protoplast Preparation and Regeneration of a Medicinal Fungus Antrodia cinnamomea
Abstract
Antrodia cinnamomea is a unique medicinal fungus in Taiwan. It has been found rich in some pharmacologically active compounds for anti-cancer, hangover, and immune regulation etc. With the in-depth study of these components, it would be interesting and important to establish a molecular system for basic studies of A. cinnamomea. Thus, we would like to set up a foundation for this purpose by studying the A. cinnamomea protoplast preparation and regeneration. Firstly, we studied the optimization method of protoplast preparation of A. cinnamomea, and found various factors that may affect the yield during protoplast preparation, such as mycelial ages, pH values, and osmotic stabilizers. Secondly, in the regeneration of protoplasts, we explored the effects of various conditions on the regeneration of protoplasts, including different media and osmotic pressure. In addition, we found that citrate buffer with pH value around 3 dramatically increased the regeneration of protoplasts of A. cinnamomea, and provided a set of regeneration methodology for A. cinnamomea.
Figures 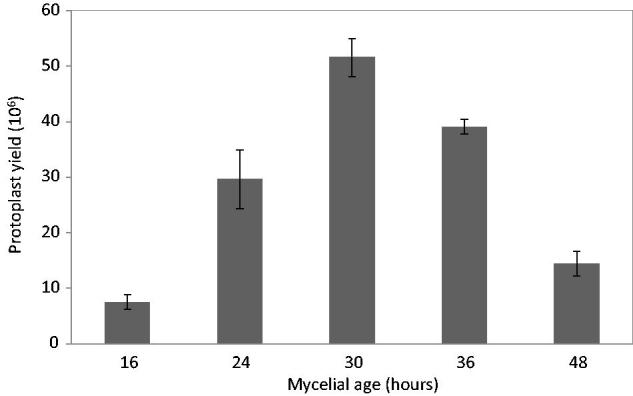
Figure 1.
The effects of fungal ages…
Figure 1.
The effects of fungal ages on protoplast yields of A. cinnamomea . The…
Figure 1. The effects of fungal ages on protoplast yields of A. cinnamomea. The fungal samples were from different cultural time of conidia at 16, 24, 30, 36 and 48 h, respectively. Digestive solution contained 0.9 M sucrose, 50 mM citrate buffer at pH 6.0, and 20 mg mL−1 lysing enzyme.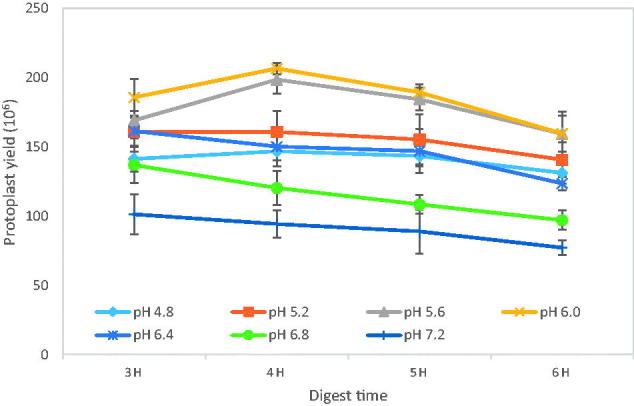
Figure 2.
The pH effects of digestive…
Figure 2.
The pH effects of digestive solution on A. cinnamomea protoplast yields. A total…
Figure 2. The pH effects of digestive solution on A. cinnamomea protoplast yields. A total of 2 × 108 30 h old germlings were digested in digestive solution with 20 mg mL−1 lysing enzyme and 1.1 M MgSO4 at different pH buffers. The pH buffers were prepared with 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer at pH 7.2, pH 6.8 and pH 6.4, and with 50 mM citrate buffer at pH 6.0, pH 5.6, pH 5.2 and pH 4.8.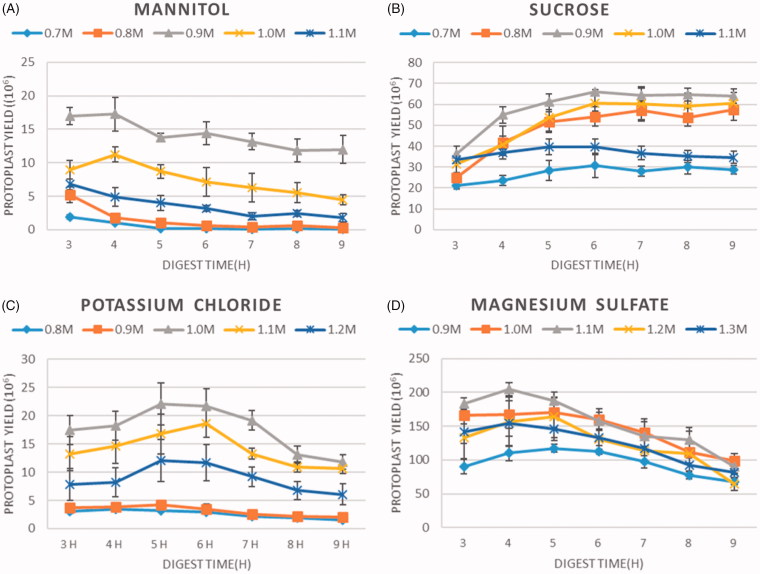
Figure 3.
Effects of osmotic stabilizers on…
Figure 3.
Effects of osmotic stabilizers on A. cinnamomea protoplast yields. Four osmotic stabilizers were…
Figure 3. Effects of osmotic stabilizers on A. cinnamomea protoplast yields. Four osmotic stabilizers were tested for the protoplast preparation, including mannitol (A), sucrose (B), KCl (C), and MgSO4 (D). Each reaction mix contained 20 mg mL−1 lysing enzyme, 50 mM citrate buffer at pH 6.0, and 2 × 108 30 h old germlings.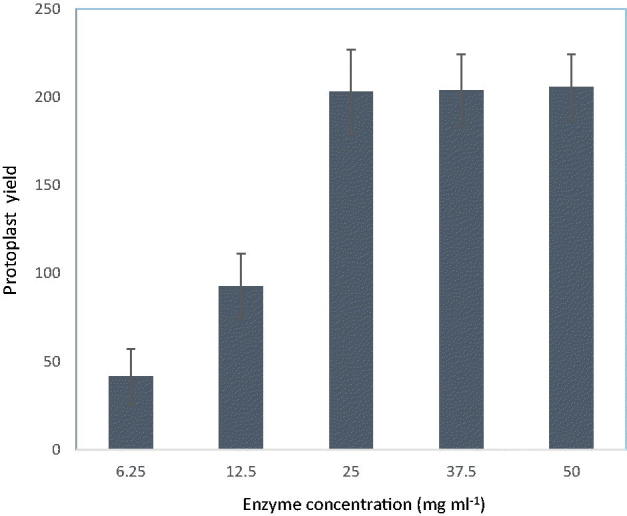
Figure 4.
Effects of digestive enzyme concentrations…
Figure 4.
Effects of digestive enzyme concentrations on A. cinnamomea protoplast yields. The reaction mixes…
Figure 4. Effects of digestive enzyme concentrations on A. cinnamomea protoplast yields. The reaction mixes contained 2 × 108 30 h old germlings mL−1 with 1.1 M MgSO4, 50 mM citrate buffer at pH 6.0 and 5 different concentrations of lysing enzyme at 6.25, 12.5, 25, 37.5 and 50 mg mL−1.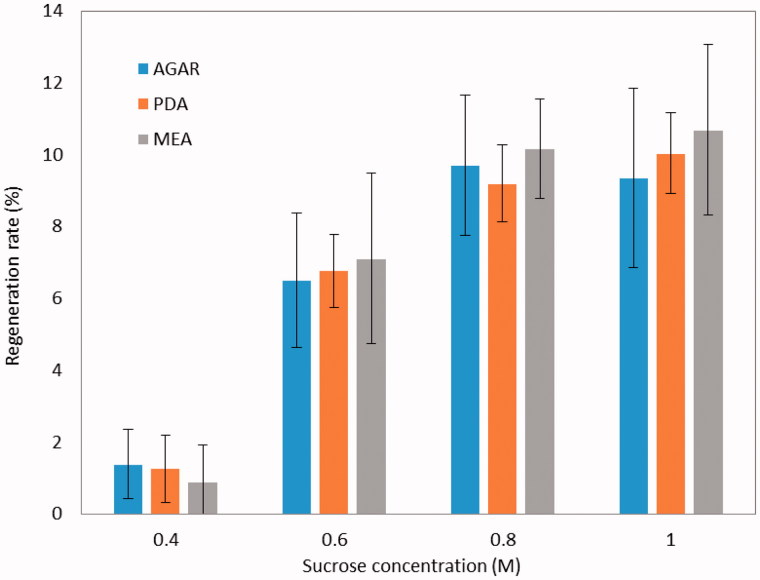
Figure 5.
Protoplast regeneration in solid media…
Figure 5.
Protoplast regeneration in solid media with different nutrient sources (MEA, PDA, and nutrient-free…
Figure 5. Protoplast regeneration in solid media with different nutrient sources (MEA, PDA, and nutrient-free 2% agar) and osmotic pressures (0.4 M, 0.6 M, 0.8 M and 1.0 M sucrose). The protoplasts were cultured in the dark at 25 °C for 7 days.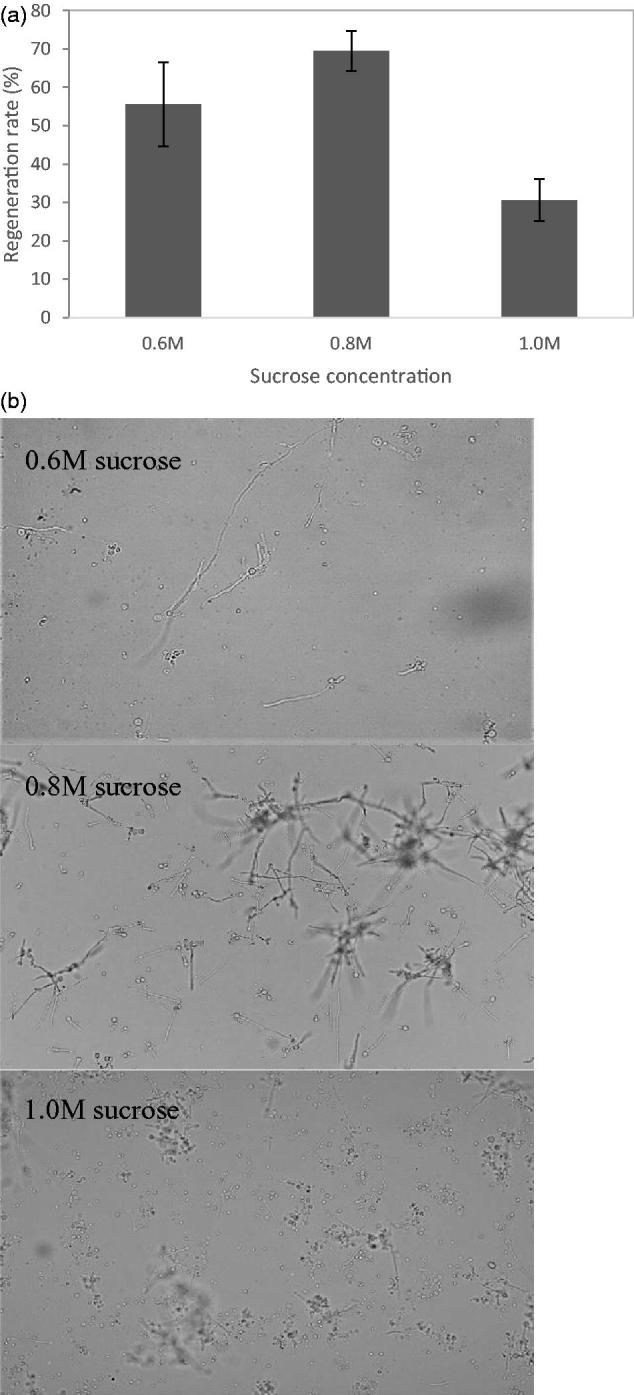
Figure 6.
The osmotic pressure effects for…
Figure 6.
The osmotic pressure effects for protoplast regeneration in liquid culture. The A. cinnamomea…
Figure 6. The osmotic pressure effects for protoplast regeneration in liquid culture. The A. cinnamomea was cultured in MEB medium containing 0.6 M, 0.8 M and 1.0 M sucrose, respectively, in addition to a final concentration of 50 mM citrate buffer at pH 3, 25 rpm shaking for 2 days at 27 °C.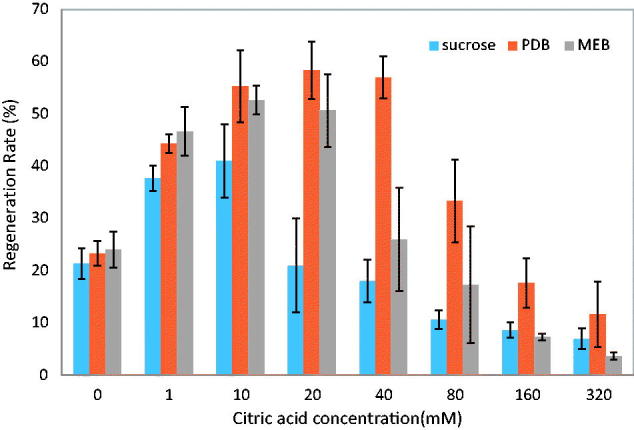
Figure 7.
Effects of citric acid concentrations…
Figure 7.
Effects of citric acid concentrations in three different nutrient sources, PDB, MEB and…
Figure 7. Effects of citric acid concentrations in three different nutrient sources, PDB, MEB and nutrient-free medium, on A. cinnamomea protoplast regeneration in liquid culture.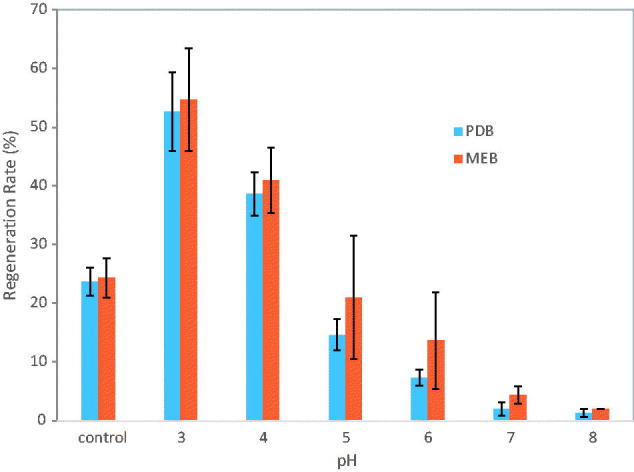
Figure 8.
Effects of pH values on…
Figure 8.
Effects of pH values on A. cinnamomea protoplast regeneration in PDB and MEB…
Figure 8. Effects of pH values on A. cinnamomea protoplast regeneration in PDB and MEB cultures with 0.8 M sucrose. The pH 3, pH 4, pH 5 and pH 6 buffers were prepared with a final concentration of 50 mM citrate buffer, and phosphate buffer for pH 7 and pH 8. A culture medium without pH buffer is used as a control (MEB with initial pH 5.1; PDB with initial pH 4.9).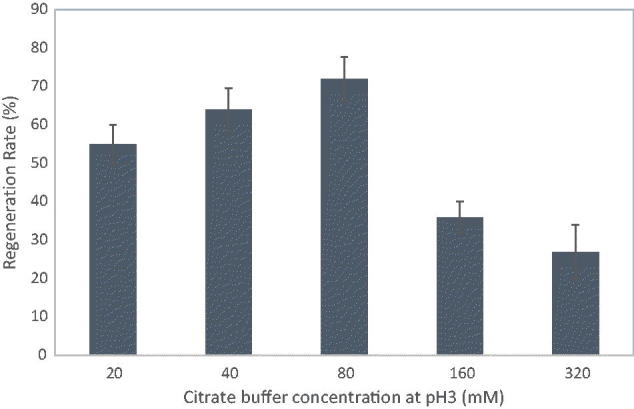
Figure 9.
Effects of citric acid concentration…
Figure 9.
Effects of citric acid concentration at pH3 on A. cinnamomea protoplast regeneration in…
Figure 9. Effects of citric acid concentration at pH3 on A. cinnamomea protoplast regeneration in PDB with 0.8 M sucrose.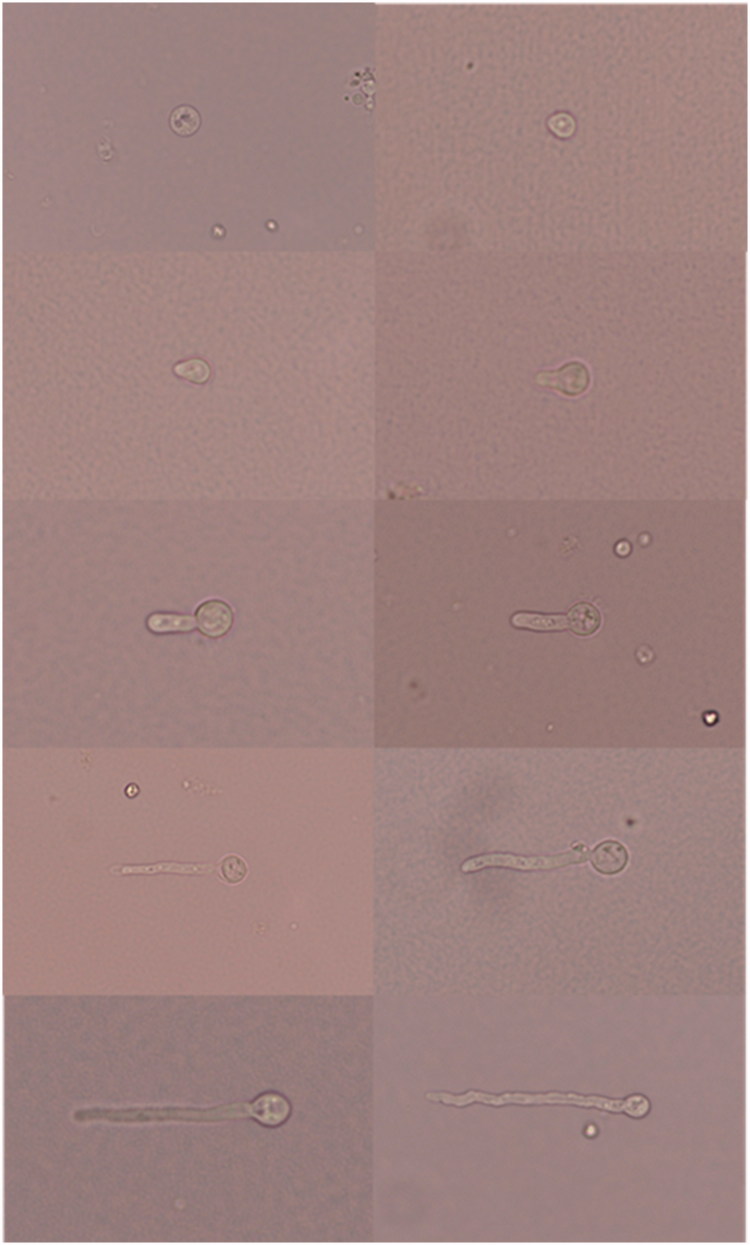
Figure 10.
The morphogenesis of A. cinnamomea…
Figure 10.
The morphogenesis of A. cinnamomea protoplast regeneration under optimal protoplast regeneration condition.
Figure 10. The morphogenesis of A. cinnamomea protoplast regeneration under optimal protoplast regeneration condition. All figures (10)