Combination of cut-log cultivated fruiting body and solid-state cultured mycelia of Taiwanofungus camphoratus ameliorates CCl4-induced liver injury in rats
Abstract
Taiwanofungus camphoratus, a medicinal mushroom indigenous to Taiwan, possesses various pharmacological functions. The most recognized ethnopharmacological relevance of T. camphoratus is hepatoprotection since it was traditionally used for treating liver disorders by Taiwan aborigines. The aim of this study is to evaluate the hepatoprotective effect of the combination of fruiting body and solid-state cultured mycelia of T. camphoratus (LDAC) on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced chronic liver damage in rats. We treated Wistar rats daily with low, medium and high [87.5, 175 and 437.5 mg/kg body weight (bw), respectively] doses of LDAC for 9 weeks. After the first week of treatment, rats were administered 20% CCl4 (0.5 mL/0.3 kg bw) twice a week to induce liver damage until the treatment ended. The results showed that administration of LDAC by oral gavage significantly reduced the absolute weight of the liver and the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in CCl4-treated rats. The activities of the antioxidant enzymes glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GRd) and catalase (CAT) were increased by LDAC treatment. Moreover, LDAC improved CCl4-induced hepatic vacuolization, necrosis and fibrosis in a dose-dependent manner, and no adverse effects were observed in the LDAC-treated groups. Based on the results, LDAC is a promising hepatoprotective agent for preventing and ameliorating CCl4-induced chronic liver injury, and this effect might be exerted through activation of the antioxidant defense system.
Figures 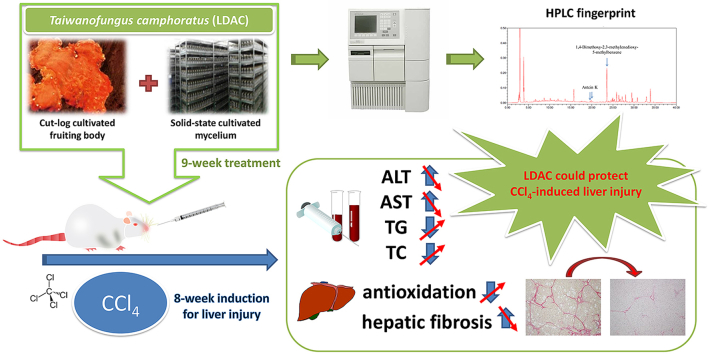
Graphical abstract
Graphical abstract
Graphical abstract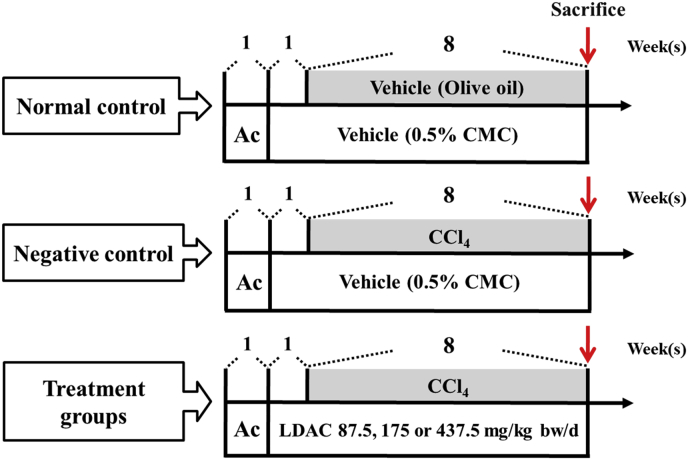
Fig. 1
Schematic diagrams showing the design…
Fig. 1
Schematic diagrams showing the design for studying the protective activity of LDAC against…
Fig. 1 Schematic diagrams showing the design for studying the protective activity of LDAC against CCl4-induced liver injury in rats. The treatments of animals are detailed in the “Materials and Methods” section. Ac, acclimatization; CMC, carboxymethyl cellulose; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; LDAC, the combination of fruiting body and solid-state cultured mycelia of Taiwanofungus camphoratus.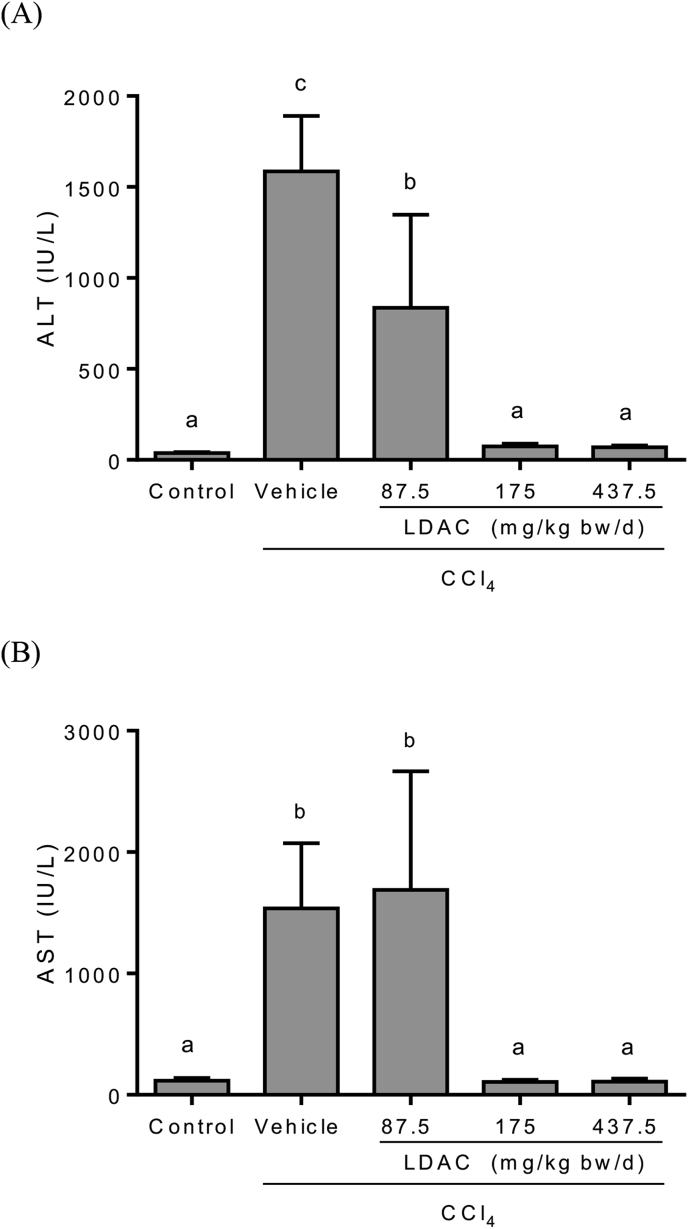
Fig. 2
Effects of LDAC on serum…
Fig. 2
Effects of LDAC on serum (A) alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and (B) aspartate transferase…
Fig. 2 Effects of LDAC on serum (A) alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and (B) aspartate transferase (AST) levels in CCl4-treated rats. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 10). Values with different superscripts are significantly different among groups according to one-way analysis of variance coupled with the Duncan multiple comparison test (p < 0.05).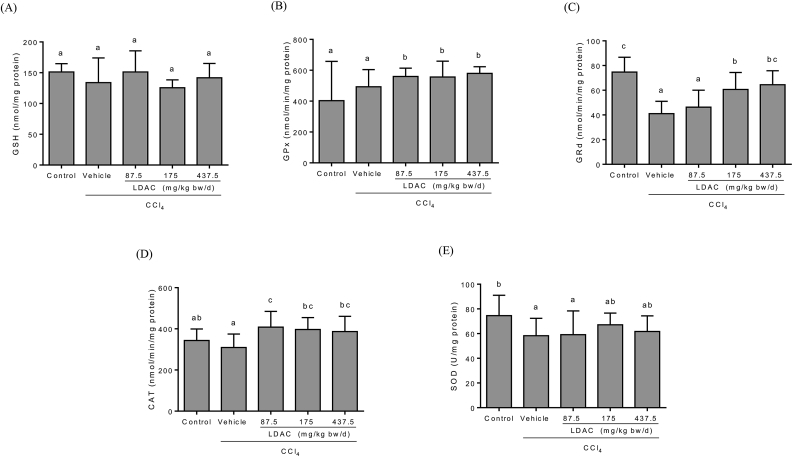
Fig. 3
Effects of LDAC on liver…
Fig. 3
Effects of LDAC on liver glutathione levels and antioxidant enzymes in CCl 4…
Fig. 3 Effects of LDAC on liver glutathione levels and antioxidant enzymes in CCl4-treated rats. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 10). Values with different superscripts are significantly different among groups according to one-way analysis of variance coupled with the Duncan multiple comparison test (p < 0.05). CAT, catalase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GRd, glutathione reductase; GSH, glutathione; SOD, superoxide dismutase.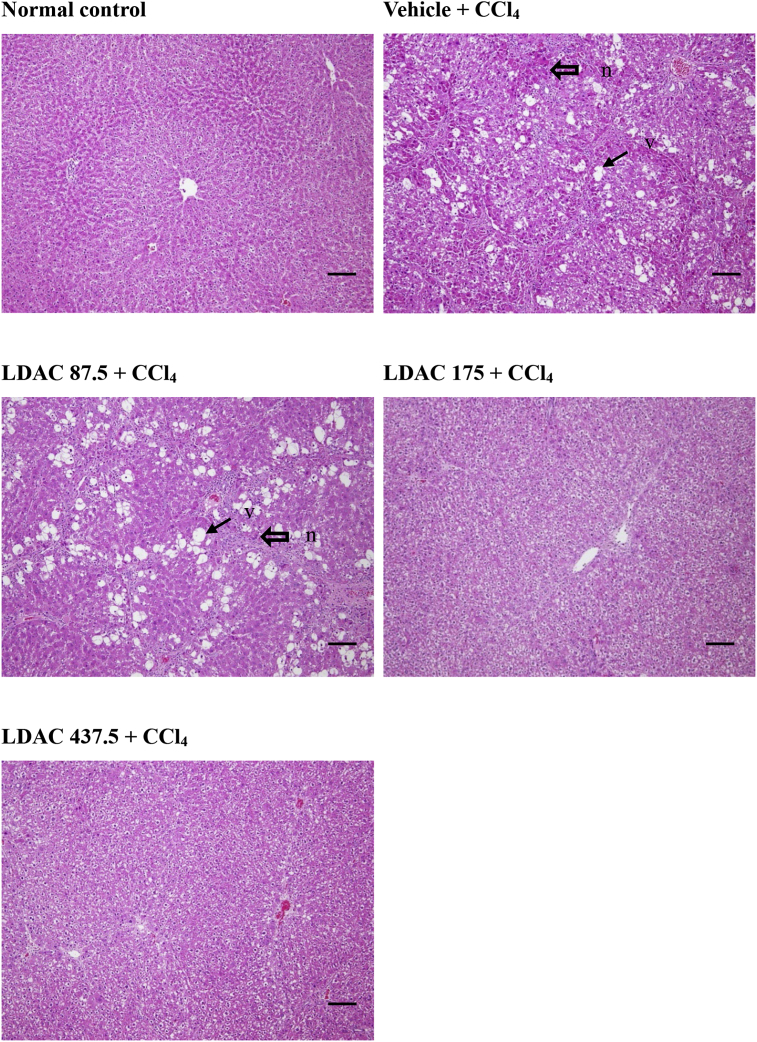
Fig. 4
Histopathological images of CCl 4…
Fig. 4
Histopathological images of CCl 4 -induced hepatic vacuolization (arrow) and necrosis (open arrow)…
Fig. 4 Histopathological images of CCl4-induced hepatic vacuolization (arrow) and necrosis (open arrow) in rats. Livers were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and visualized at 100x magnification. Abbreviations of groups are as in Table 1. Bar = 100 μm. v: vacuolization; n: necrosis.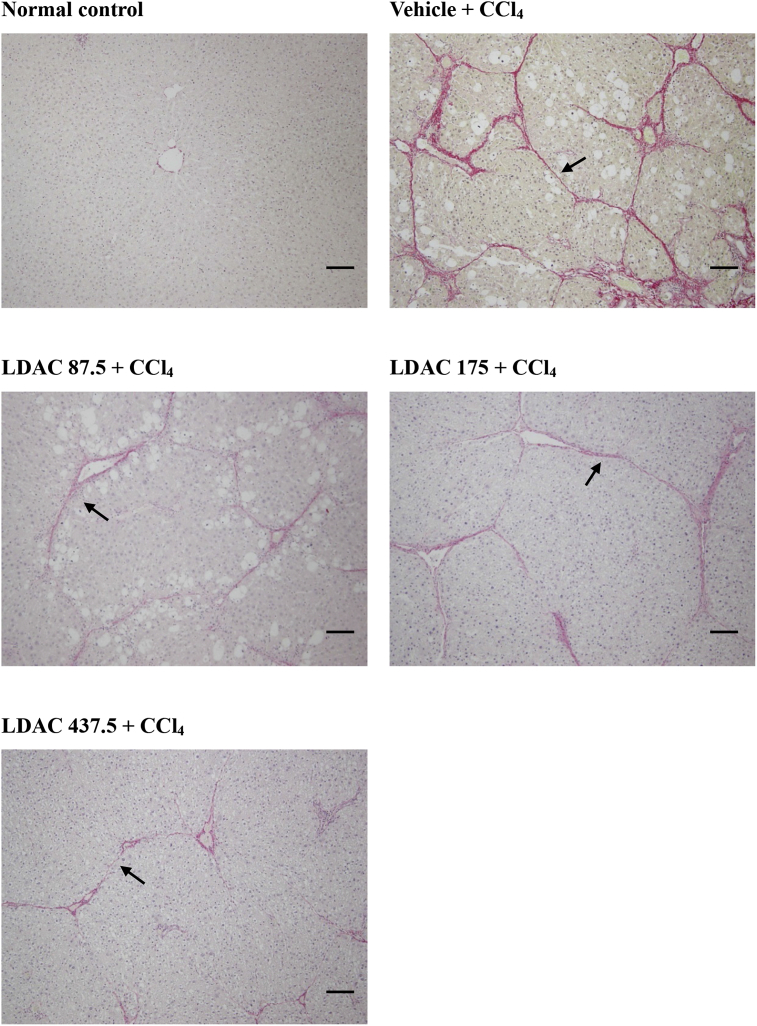
Fig. 5
Histopathological photographs of CCl 4…
Fig. 5
Histopathological photographs of CCl 4 -induced hepatic fibrosis (arrow) treated with LDAC in…
Fig. 5 Histopathological photographs of CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis (arrow) treated with LDAC in rats. Livers were stained with Sirius red and visualized at 100x magnification. Abbreviations of groups are as in Table 1. Bar = 100 μm.