4-Acetylantroquinonol B inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine release and alleviates sepsis through of MAPK and NFκB suppression
Abstract
Figures 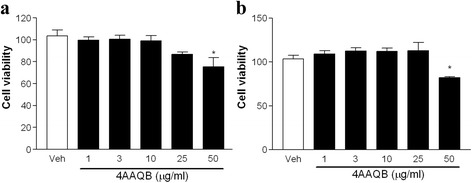
Fig. 1
Effect of 4AAQB on cell…
Fig. 1
Effect of 4AAQB on cell viability of murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharides (LPS).…
Fig. 1 Effect of 4AAQB on cell viability of murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharides (LPS). RAW264.7 macrophages (a) or peritoneal macrophages (b) were incubated with various concentrations of 4AAQB in the presence of LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M of three independent experiments and *p < 0.05 as compared with DMSO vehicle group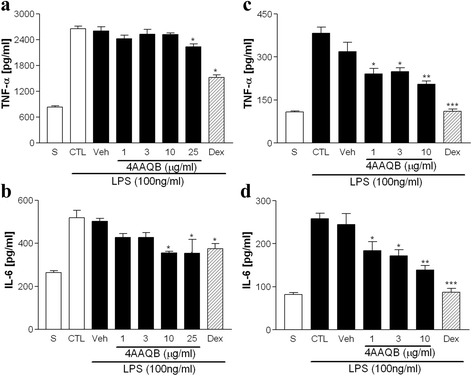
Fig. 2
Effect of 4AAQB on TNFα…
Fig. 2
Effect of 4AAQB on TNFα and IL-6 production in LPS-stimulated macrophages. RAW264.7 macrophages…
Fig. 2 Effect of 4AAQB on TNFα and IL-6 production in LPS-stimulated macrophages. RAW264.7 macrophages (a, b) or peritoneal macrophages (c, d) were pretreated with various concentrations of 4AAQB of dexamethasone (Dex, 10 μM) for 30 min, and then activated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. The TNFα and IL-6 concentrations were measured by ELISA kits. Results are showed as mean ± S.E.M of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 as compared with LPS-treated groups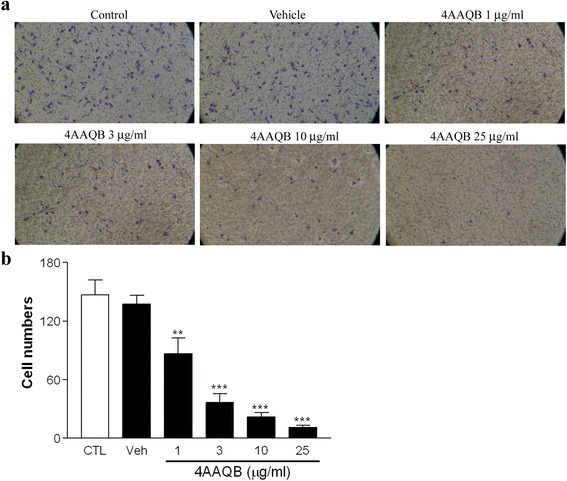
Fig. 3
Effect of 4AAQB on LPS-induced…
Fig. 3
Effect of 4AAQB on LPS-induced cell migration of murine macrophages. Peritoneal macrophages were…
Fig. 3 Effect of 4AAQB on LPS-induced cell migration of murine macrophages. Peritoneal macrophages were pretreated with various concentrations of 4AAQB for 30 min and then activated with LPS. The results of cell migrated through gelatin-coated transwells for 20 h were shown (a), and the migrated cells were counted (b). Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M of three independent experiments. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 as compared with LPS-treated control groups (CTL)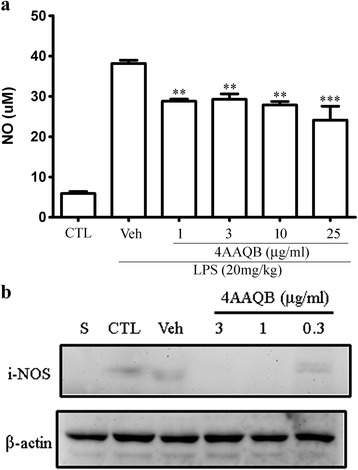
Fig. 4
The effects of 4AAQB on…
Fig. 4
The effects of 4AAQB on LPS-induced nitric oxide production and iNOS expression in…
Fig. 4 The effects of 4AAQB on LPS-induced nitric oxide production and iNOS expression in RAW264.7 macrophages. a The cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) only or with various concentrations of 4AAQB and the nitric oxide production was measured after 24 h. Control (CTL) values were obtained in the absence of LPS. Data were obtained from three independent experiments and expressed as means ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05 compared with the LPS-activated only group. b RAW264.7 cells were treated with various concentration of 4AAQB and stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml). Cells were harvested and iNOS was detected. Each experiment has been performed three times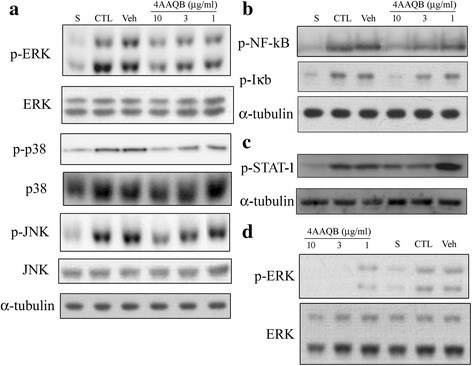
Fig. 5
Effects of 4AAQB on the…
Fig. 5
Effects of 4AAQB on the LPS-induced activation of MAP kinases, IkBα, NFκB p65…
Fig. 5 Effects of 4AAQB on the LPS-induced activation of MAP kinases, IkBα, NFκB p65 and STAT1 in RAW 264.7 macrophages and peritoneal macrophages. RAW264.7 cells were treated with various concentration of 4AAQB and stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 30 min. Cells were harvested and total cell extracts were prepared. a Phosphorylated-ERK, phosphorylated-JNK, phosphorylated-p38, or b Phosphorylated-IκBα and NFκB p65 subunit and c Phosphorylated-STAT1 were detected by Western blot analysis. Total ERK, JNK, p38 and α-tubulin were used as internal standard. d Peritoneal macrophages were treated with various concentration of 4AAQB and stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 30 min. Phosphorylated-ERK and total ERK were detected by Western blot analysis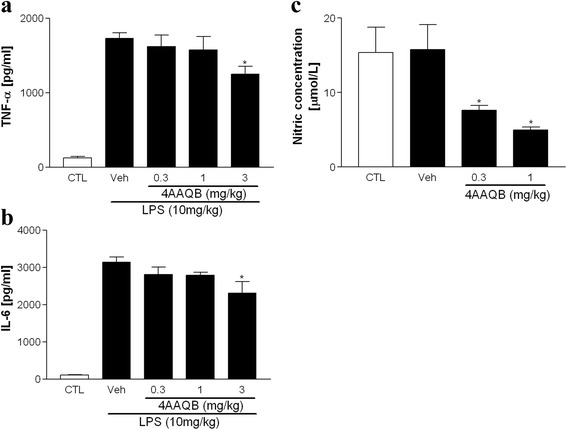
Fig. 6
The effects of 4AAQB on…
Fig. 6
The effects of 4AAQB on LPS-induced cytokines and NO release. ICR mice (25–30…
Fig. 6 The effects of 4AAQB on LPS-induced cytokines and NO release. ICR mice (25–30 g) were treated with 4AAQB and induction of endotoxemia with LPS (20 mg/kg) after 30 min. After 24 h, mice were euthanized collect blood by cardiac puncture. The serum was obtained and the cytokines TNFα/IL-6 (a and b) and NO (c) were measured. Values are presented as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 10). *p < 0.05 as compared with the LPS-activated group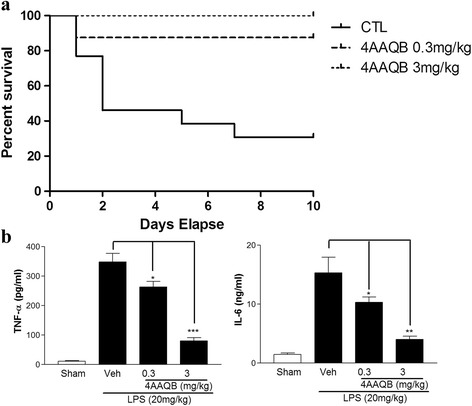
Fig. 7
The protective effects of 4AAQB…
Fig. 7
The protective effects of 4AAQB on survival rate, cytokine production and tissue inflammation…
Fig. 7 The protective effects of 4AAQB on survival rate, cytokine production and tissue inflammation induced by CLP operation in vivo. Mice were administered with 4AAQB (0.3 and 3 mg/kg, i.p., n = 8) in DMSO or DMSO (CTL, n = 13) for 30 min, and then conducted CLP operation. a Survival was monitored for up to 10 days. Values are presented as mean + S.E.M. *p < 0.05 as compared with the LPS-activated group. b Mice were anesthetized and blood was collected for serum isolation 24 h after CLP operation, and concentration of cytokines was measured by ELISA. Values are presented mean + S.E.M. and *p < 0.05 compared with LPS-treated control group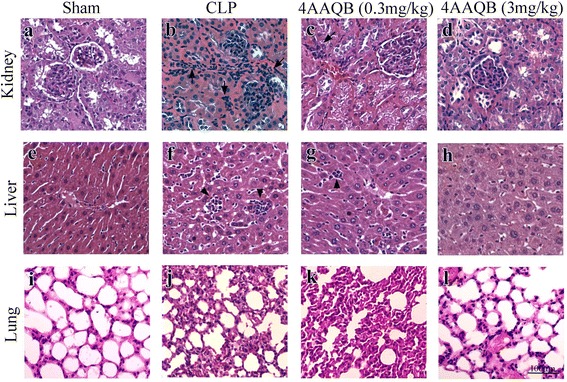
Fig. 8
Protective effects of 4AAQB on…
Fig. 8
Protective effects of 4AAQB on tissue injury in a CLP-induced sepsis model. Morphological…
Fig. 8 Protective effects of 4AAQB on tissue injury in a CLP-induced sepsis model. Morphological changes in the mouse kidney (a-d), liver (e-h) lung (i-l), and sections [hematoxylin and eosin (h & e) stain, all panels are × 400 with the same scale bar in panel L]. a, e, k control mice (Sham), b, f, j CLP-induced sepsis mice, c, g, k CLP-induced sepsis mice treated with low dose 4AAQB (0.3 mg/kg) and d, h, l CLP-induced sepsis mice treated with high dose 4AAQB (3 mg/kg) All figures (8)