An efficient total synthesis of a potent anti-inflammatory agent, benzocamphorin F, and its anti-inflammatory activity
Abstract
A naturally occurring enynyl-benzenoid, benzocamphorin F (1), from the edible fungus Taiwanofungus camphoratus (Antrodia camphorata) was characterized by comprehensive spectral analysis. It displays anti-inflammatory bioactivity and is valuable for further biological studies. The present study is the first total synthesis of benzocamphorin F and the developed strategy described is a more efficient procedure that allowe the large-scale production of benzocamphorin F for further research of the biological activity both in vitro and in vivo.
Figures 
Figure 1
Structure of benzocamphorin F (…
Figure 1
Structure of benzocamphorin F ( 1 ).
Figure 1 Structure of benzocamphorin F (1).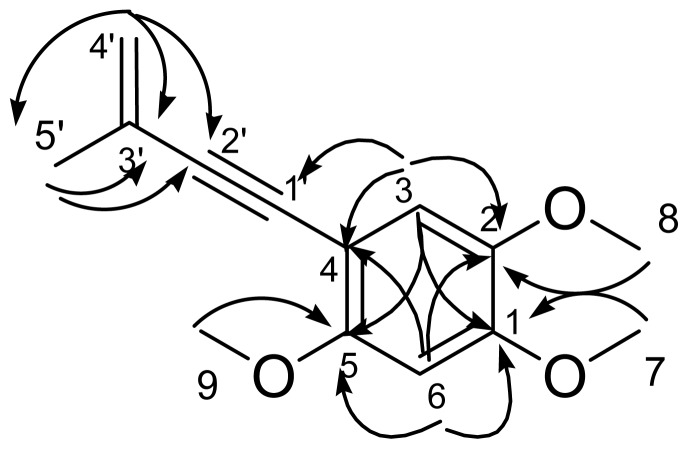
Figure 2
Heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation (HMBC) (→)…
Figure 2
Heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation (HMBC) (→) correlations for benzocamphorin F ( 1 ).
Figure 2 Heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation (HMBC) (→) correlations for benzocamphorin F (1).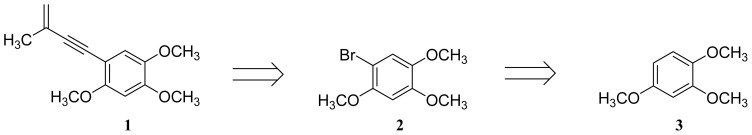
Figure 3
Retrosynthetic analysis of benzocamphorin F…
Figure 3
Retrosynthetic analysis of benzocamphorin F ( 1 ).
Figure 3 Retrosynthetic analysis of benzocamphorin F (1).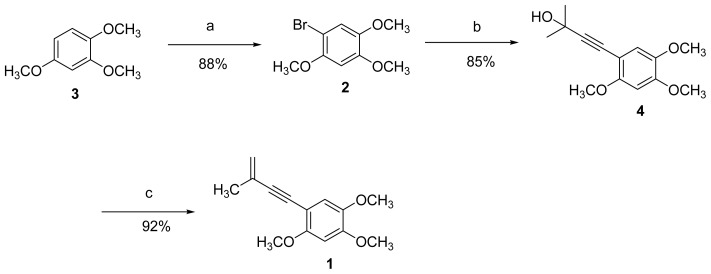
Figure 4
Synthesis of benzocamphorin F (…
Figure 4
Synthesis of benzocamphorin F ( 1 ). Reagents and conditions: a ) NBS,…
Figure 4 Synthesis of benzocamphorin F (1). Reagents and conditions: a) NBS, acetonitrile, room temp; b) 2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol, Pd(PPh3)4, CuI, DMF; c) methanesulfonyl chloride, toluene, microwave.