The Leaf Extracts of Toona sinensis and Fermented Culture Broths of Antrodia camphorata Synergistically Cause Apoptotic Cell Death in Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells
Abstract
Toona sinensis is a common edible vegetable that is used in certain Chinese dishes and has importance in folk medicine. The leaf extracts of T sinensis possess and exhibit anticancer efficacy against various cancer cell types. In Taiwanese folklore, Antrodia camphorata, also known as "Niu-Cheng-Zi," is used in traditional medicine to treat various illnesses. Its fruit and mycelium possess various potent antiproliferative properties. Two studies from our group have reported that T sinensis or A camphorata has the ability to cause apoptosis in various cancer cells. Conversely, underlying molecular mechanisms and any beneficial effects remain unknown. This study shows anticancer efficacy for both T sinensis and A camphorata co-treatments that target HL-60 cells. The combination index values indicate that 40 µg/mL of T sinensis and 25 µg/mL of A camphorata as a combined treatment shows a synergetic effect, which reduces HL-60 cell proliferation. Alternately, this treatment exhibited no cytotoxic effects for human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Western blot data showed that T sinensis and A camphorata as a combined treatment result in augmented expression of apoptosis, cytochrome c release, Bcl-2 inhibition, expression of Bax, Fas, and FasL, as well as the cleavage of Bid in HL-60 cells. Moreover, this combined treatment overshadowed monotherapy in its ability to inhibit uPAR, MMP-9, MMP-2, COX-2 expression, and PGE2 secretions. Our study strongly implies that this combined treatment offers more beneficial effects to suppress and treat leukemia due to apoptosis-mediated cell inhibition. Further in vivo studies related to the combined treatment could establish its future potential.
Figures 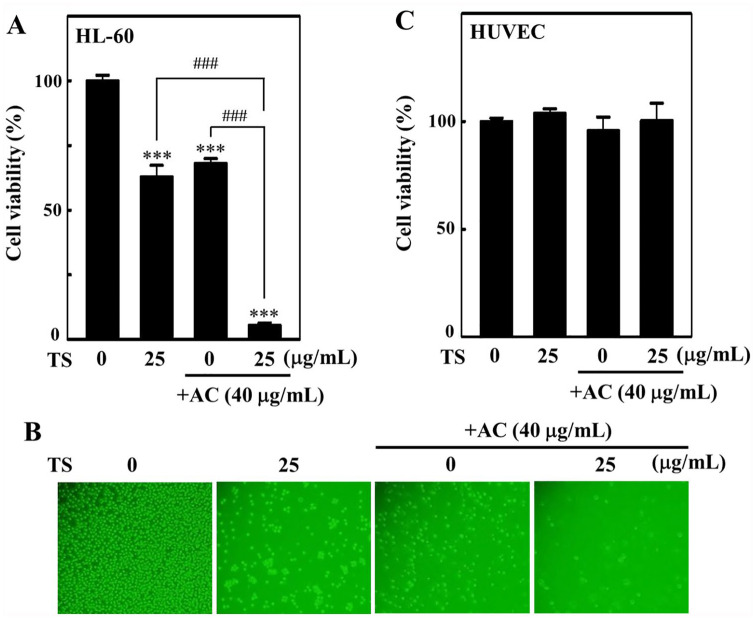
Figure 1.
Effect of Toona sinensis and…
Figure 1.
Effect of Toona sinensis and Antrodia camphorata co-treatment on HL-60 cell viability. (A,…
Figure 1. Effect of Toona sinensis and Antrodiacamphorata co-treatment on HL-60 cell viability. (A, B)HL-60 cells were treated with 25 µg/mL T sinensis or 40µg/mL A camphorata or in combination for 24 hours.Morphological changes were observed under the phase-contrast microscope(200× magnification). Using the trypan blue exclusion assay, HL-60 cellviability was determined. (C) HUVECs (human umbilical vein endothelialcells) were treated with 25 µg/mL T sinensis or 40µg/mL A camphorata or combination of both for 24 hoursand then the cell viability was measured. Values were expressed as mean± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance was assigned as***P < .001 compared with untreated controlcells and ###P < .001 compared withT sinensis or A camphorata alonetreated cells.
Figure 2.
Effect of Toona sinensis and/or…
Figure 2.
Effect of Toona sinensis and/or Antrodia camphorata treatment on sub-G 1 cell cycle…
Figure 2. Effect of Toona sinensis and/or Antrodiacamphorata treatment on sub-G1 cell cycle ofHL-60 cells. (A) HL-60 cells were treated with 25 µg/mL Tsinensis or 40 µg/mL A camphorata or incombination for 24 hours and then analyzed by flow cytometry. (B)Percentage of sub-G1 cell distribution after Tsinensis, A camphorata, treatments were presented. Allvalues are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statisticalsignificance was assigned as ***P < .001 comparedwith untreated control cells and ###P <.001 compared with T sinensis or Acamphorata alone treated cells.
Figure 3.
Toona sinensis and/or Antrodia camphorata…Figure 3.
Toona sinensis and/or Antrodia camphorata treatment induced the release of cytochrome c in… Figure 3. Toona sinensis and/or Antrodiacamphorata treatment induced the release of cytochrome c inHL-60 cells. HL-60 cells were treated with 25 µg/mL Tsinensis or 40 µg/mL A camphorata or incombination for 24 hours. The expression of cytosolic cytochromec, caspase-3, and PARP proteins were measured byWestern blot method using β-actin as an internal control. Densitometricanalysis was performed using the AlphaEase (Genetic Technology Inc) withthe value of control assigned as 1.
Figure 4.
Effect of Toona sinensis and/or…
Figure 4.
Effect of Toona sinensis and/or Antrodia camphorata treatment on Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in HL-60…
Figure 4. Effect of Toona sinensis and/or Antrodiacamphorata treatment on Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in HL-60 cells.HL-60 cells were treated with 25 µg/mL T sinensis or 40µg/mL A camphorata or in combination for 24 hours. Theexpression of Bax, Bcl-2 proteins were measured by Western blot usingβ-actin as an internal control. Densitometric analysis was performedusing the AlphaEase (Genetic Technology Inc) with the value of controlassigned to be 1.
Figure 5.
Effect of Toona sinensis and/or…
Figure 5.
Effect of Toona sinensis and/or Antrodia camphorata treatment on HL-60 cell mitochondria membrane…
Figure 5. Effect of Toona sinensis and/or Antrodiacamphorata treatment on HL-60 cell mitochondria membranepotential. (A, B) HL-60 cells were treated with 25 µg/mL Tsinensis and/or 40 µg/mL A camphorata for24 hours, followed by measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential byflow cytometry. The percentage of mitochondrial membrane potential wasindicated by DiOC6 fluorescence. All the values are expressedin mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significance wasassigned as ***P < .001 compared with untreatedcontrol cells and ###P < .001 comparedwith T sinensis or A camphorata alonetreated cells.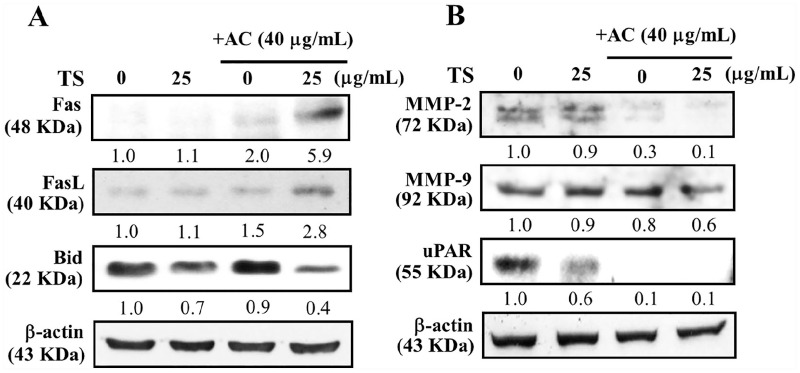
Figure 6.
Effects of Toona sinensis and/or…
Figure 6.
Effects of Toona sinensis and/or Antrodia camphorata treatment on the expression of various…
Figure 6. Effects of Toona sinensis and/or Antrodiacamphorata treatment on the expression of varioustumorigenic proteins in HL-60 cells. HL-60 cells were treated with 25µg/mL T sinensis or 40 µg/mL Acamphorata or in combination for 24 hours. Western blotmethod was used to measure (A) Fas, FasL, and Bid proteins; and (B)MMP-2, MMP-9, and uPAR proteins. All values were expressed as mean ±standard deviation (n = 3). β-actin was used as an internal control.Densitometric analysis was performed using the AlphaEase (GeneticTechnology Inc) with the value of control assigned to be 1.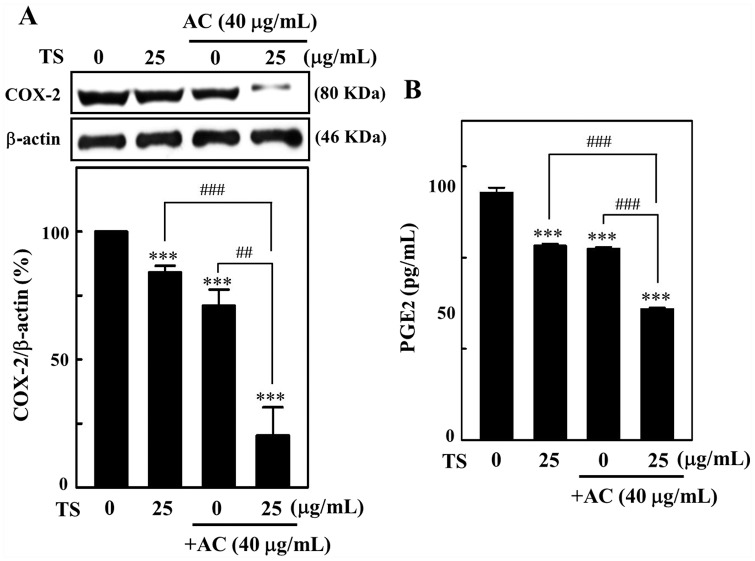
Figure 7.
Toona sinensis and Antrodia camphorata…Figure 7.
Toona sinensis and Antrodia camphorata co-treatment has downregulated the expression of COX-2 and… Figure 7. Toona sinensis and Antrodia camphorataco-treatment has downregulated the expression of COX-2 andPGE2 production in HL-60 cells. HL-60 cells were treatedwith T sinensis (25 µg/mL), Acamphorata (40 µg/mL), and T sinensis +A camphorata for 24 hours. (A) Western blot methodwas used to measure the expression of COX-2 protein. AlphaEase (GeneticTechnology Inc) was used for the densitometric analysis. Control valuewas assigned as one. (B) Using the ELISA kit method, PGE2concentration in the culture media was also determined. All values wereexpressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Statistical significancewas assigned as ***P < .001 compared with untreatedcontrol cells and ##P < .05;###P < .001 compared with Tsinensis or A camphorata alone treatedcells. All figures (7)