Physical characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study of self-assembling amphotericin B-loaded lecithin-based mixed polymeric micelles
Abstract
To alleviate the inherent problems of amphotericin B (AmB), such as poor water solubility and nephrotoxicity, a novel self-assembling mixed polymeric micelle delivery system based on lecithin and combined with amphiphilic polymers, Pluronic(®), Kolliphor(®), d-alpha tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate, and 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-methoxy(poly(ethylene glycol)-2000 (DSPE-PEG2K) was developed. An optimal formulation (Ambicelles) composed of AmB:lecithin:DSPE-PEG2K in a 1:1:10 weight ratio was obtained. The particle size, polydispersion index, drug encapsulation efficiency, and drug loading were 187.20±10.55 nm, 0.51±0.017, 90.14%, and 7.51%, respectively, and the solubility was increased from 0.001 to 5 mg/mL. Compared with that of Fungizone(®), the bioavailability of Ambicelles administered intravenously and orally increased 2.18- and 1.50-fold, respectively. Regarding the in vitro cytotoxicity, Ambicelles had a higher cell viability than free AmB solution or Fungizone(®) did. With pretreatment of 50 μg/mL ethanolic extract of Taiwanofungus camphoratus followed by AmB to HT29 colon cancer cells, the 50% inhibitory concentration of AmB solution was 12 μg/mL, whereas that of Ambicelles was 1 μg/mL, indicating that Ambicelles exerted a greater synergistic anticancer effect.
Figures 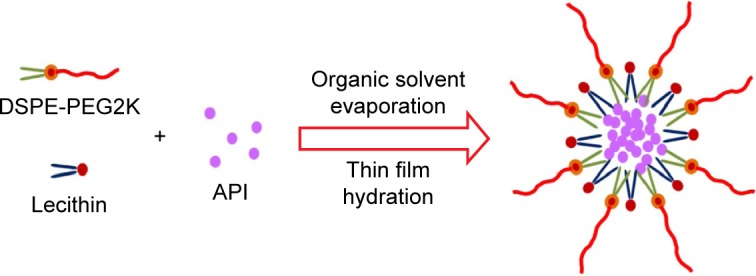
Figure 1
Scheme for preparing amphotericin B-loaded…
Figure 1
Scheme for preparing amphotericin B-loaded mixed polymeric micelles. Abbreviations: DSPE-PEG2K, 1,2-distearoyl- sn -glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-…
Figure 1 Scheme for preparing amphotericin B-loaded mixed polymeric micelles. Abbreviations: DSPE-PEG2K, 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-methoxy(poly(ethylene glycol)-2000; API, active pharmaceutical ingredients.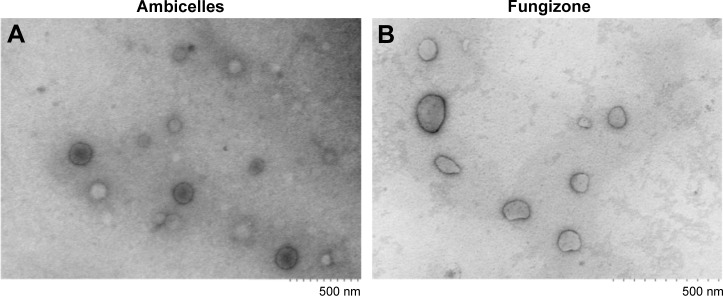
Figure 2
Transmission electron micrographs of (…
Figure 2
Transmission electron micrographs of ( A ) Ambicelles and ( B ) Fungizone…
Figure 2 Transmission electron micrographs of (A) Ambicelles and (B) Fungizone®.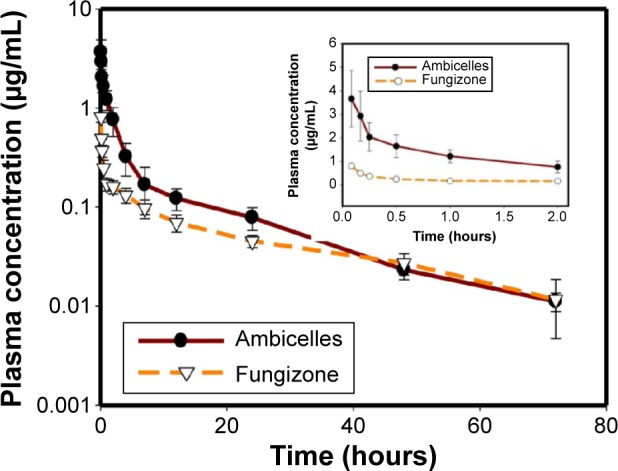
Figure 3
Plasma concentration–time curves of amphotericin…
Figure 3
Plasma concentration–time curves of amphotericin B after intravenous administration of Fungizone ® or…
Figure 3 Plasma concentration–time curves of amphotericin B after intravenous administration of Fungizone® or Ambicelles (0.8 mg/kg) to rats. Note: Each data point represents the mean ± standard deviation of three determi nations (n=3). Inset shows plasma concentration time profile from time 0 to 2 hours.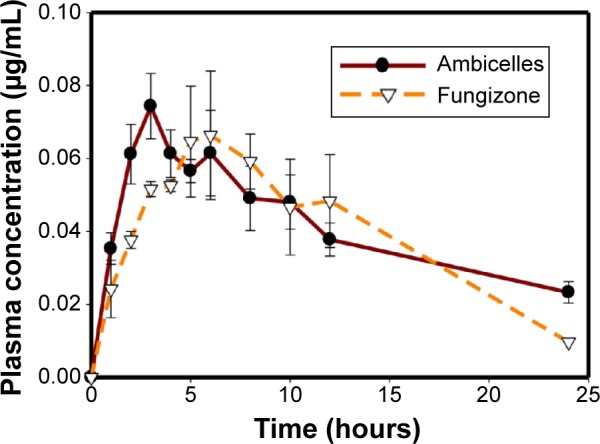
Figure 4
Plasma concentration–time curves of amphotericin…
Figure 4
Plasma concentration–time curves of amphotericin B after oral administration of Fungizone ® or…
Figure 4 Plasma concentration–time curves of amphotericin B after oral administration of Fungizone® or Ambicelles (10 mg/kg) to rats. Note: Each data point represents the mean ± standard deviation of three determinations (n=3).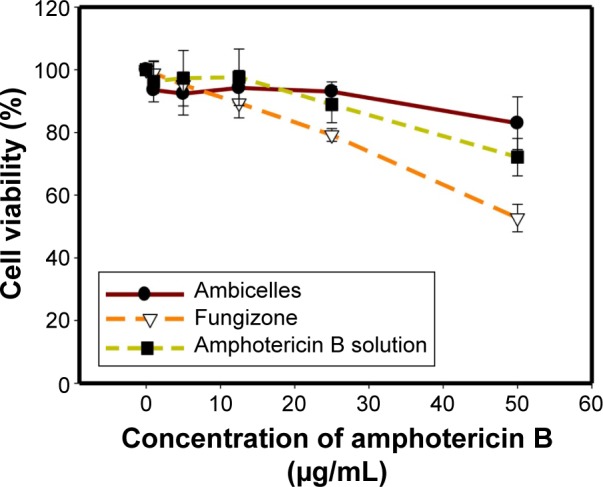
Figure 5
Viability of HT29 cells after…
Figure 5
Viability of HT29 cells after treatment with various concentrations of amphotericin B, Fungizone…
Figure 5 Viability of HT29 cells after treatment with various concentrations of amphotericin B, Fungizone®, or Ambicelles.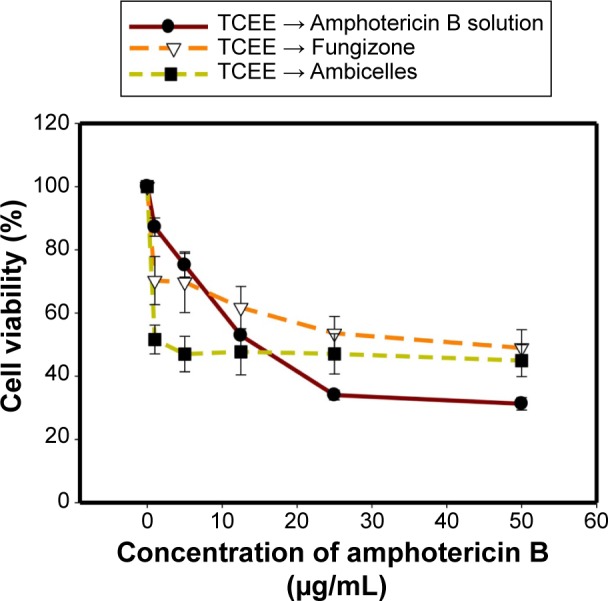
Figure 6
Viability of HT29 cells after…
Figure 6
Viability of HT29 cells after pretreatment with 50 μg/mL of Taiwanofungus camphoratus ethanolic…
Figure 6 Viability of HT29 cells after pretreatment with 50 μg/mL of Taiwanofungus camphoratus ethanolic extract (TCEE), followed by treatment with various concentrations of an amphotericin B, Fungizone®, or Ambicelles.