Chemical Composition and Chronic Toxicity of Disc-Cultured Antrodia cinnamomea Fruiting Bodies
Abstract
Antrodia cinnamomea (AC) is a popular fungus for use as folk medicine in health maintenance and disease prevention and treatment. Disc culture is a novel technique for producing AC fruiting bodies. This study aimed to investigate the bioactive components and toxicological properties of disc-cultured AC fruiting body powders (ACP) in rats. The HPLC technique was used to quantify the composition of bioactive triterpenoids in ACP. Toxicological properties were evaluated on male and female Sprague-Dawley rats receiving ACP orally at 200, 600, and 1000 mg/kg body weight for 90 days; the control group received only distilled water. The results show that ACP contained seven important AC index compounds, namely antcins A, B, C, K, and H, dehydrosulphurenic acid, and dehydroeburicoic acid. At the tested doses, oral ACP administration for 90 days caused no mortality, adverse effects on general health, body and organ weights, and food intake. Furthermore, no significant variations were observed in hematological and biochemical parameters among either sex of ACP-treated and control animals. An histopathological examination of vital organs showed no significant structural changes in organs, even in high-dose ACP-treated animals. This study indicated that ACP contained the major bioactive triterpenoids of AC fruiting bodies, and its no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) was 1000 mg/kg/day, about 20 times the recommended daily intake.
Figures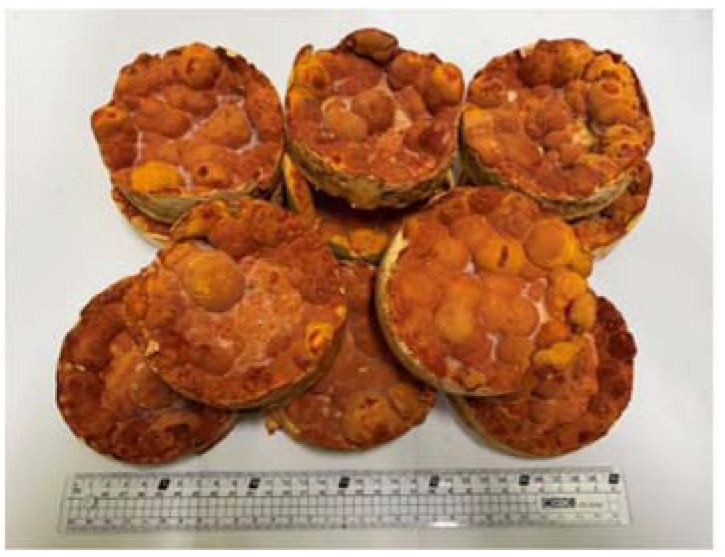 
Figure 1
Disc-cultured Antrodia cinnamomea fruiting bodies…
Figure 1
Disc-cultured Antrodia cinnamomea fruiting bodies obtained from 90 days of cultivation.
Figure 1 Disc-cultured Antrodia cinnamomea fruiting bodies obtained from 90 days of cultivation.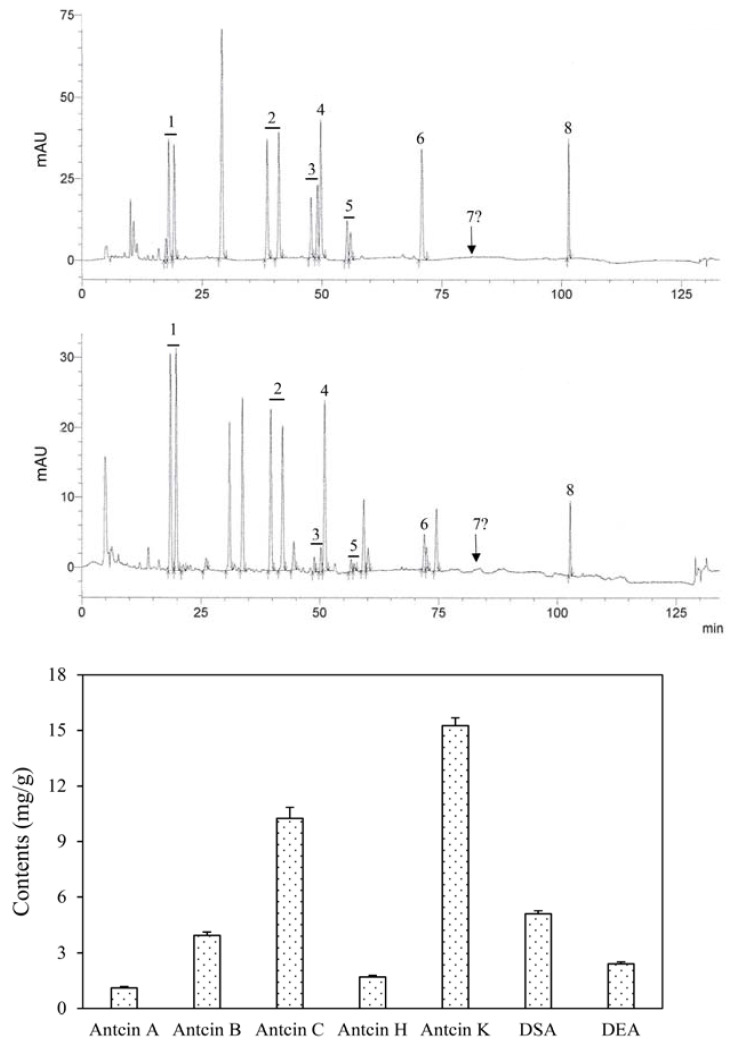
Figure 2
Representative chromatograms and contents of…
Figure 2
Representative chromatograms and contents of bioactive triterpenoid compounds in the powders of disc-cultured…
Figure 2 Representative chromatograms and contents of bioactive triterpenoid compounds in the powders of disc-cultured Antrodia cinnamomea fruiting bodies. Peaks 1 = antcin K; 2 = antcin C, 3 = antcin H, 4 = dehydrosulphurenic acid (DSA), 5 = antcin B, 6 = antcin A, 7 = 15-acetyldehydrosulphurenic acid; 8 = dehydroeburicoic acid (DEA). The underlined numbers indicate compounds that are present in both R-form and S-form, and were treated and calculated as the same compound.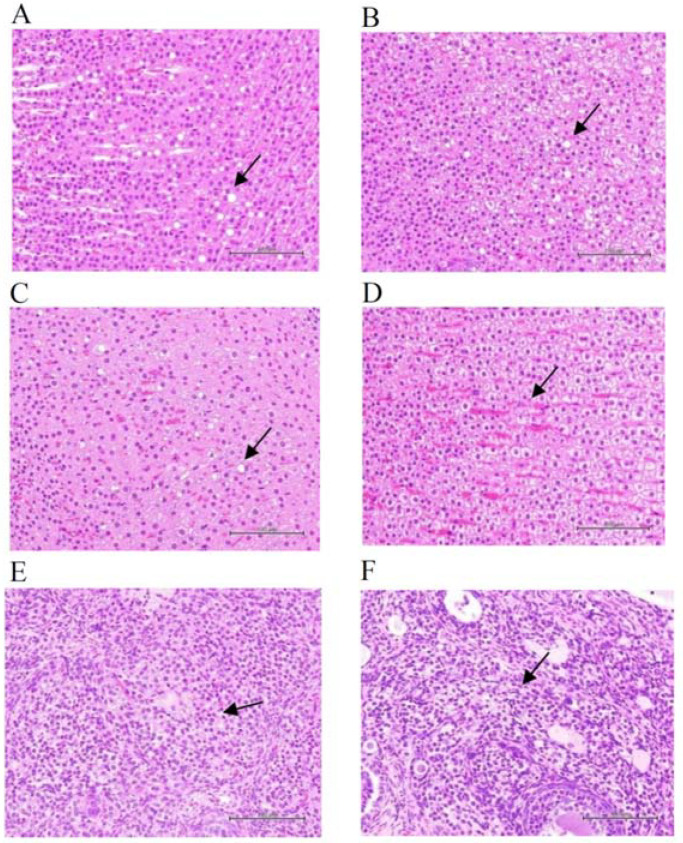
Figure 3
Histopathological changes of the adrenal…
Figure 3
Histopathological changes of the adrenal glands of male and female rats and ovaries…
Figure 3 Histopathological changes of the adrenal glands of male and female rats and ovaries of female rats receiving high-dose ACP for 90 days. Arrows indicate adrenal glands of zona fasciculate having multifocal cholesterol hypertrophy and lipidosis: in the male rats of (A) the control (animal #111) and (B) high-dose ACP-treated (animal #137) groups and the female rats of (C) the control (animal #169) and (D) high-dose ACP-treated (animal #186) groups. Arrows indicate multifocal cholesterol hypertrophy of interstitial glands in ovaries of (E) the control (animal #169) and (F) high-dose ACP-treated (animal #199) female rats. In the male rats, the mean scores of cholesterol hypertrophy and lipidosis were 2.0 ± 0.0 and 0.6 ± 0.9 in the control group, and 2.3 ± 0.6 and 0.8 ± 1.0 in the high-dose ACP-treated group, respectively. In the female rats, the mean scores of cholesterol hypertrophy and lipidosis were 1.4 ± 0.9 and 0.2 ± 0.6 in the control group and 2.1 ± 0.8 and 0 in the high-dose ACP-treated group, respectively. The mean scores of multifocal cholesterol hypertrophy of interstitial glands in the ovary were 0.2 ± 0.6 and 0.5 ± 1.0 in the control and high-dose ACP-treated groups. The scores in histopathological changes between the control and high-dose ACP-treated animals were not statistically different as analyzed by the Student’s t-test. H&E stain; 400×.